What are Biomarkers?
Biomarkers are biological characteristics which can be used to detect diseases. Researchers are interested in finding biomarkers because they can be used to help diagnose and treat patients.
Biomarkers are usually proteins found in cells or bodily fluids like blood or urine. By measuring the levels of these proteins doctors can assess how severe a disease is and detect improvements after treatment.
Example: HER-2 and breast cancer diagnosis and treatment
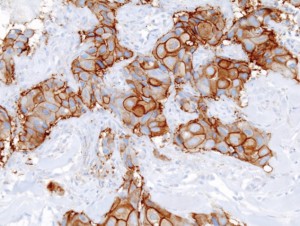
Detecting a biomarker. HER-2 proteins are stained brown, the small blue circles are cell nuclei. (source)
In some breast cancers the tumour cells have abnormally high levels of a protein called HER-2. HER-2 is a protein found on the cell surface which receives chemical signals to make the cell grow and divide. If cells have too much HER-2 the cells grow out of control, leading to cancer and tumour formation.
Detection: HER-2 positive cells are easily detected in biopsy material using a stain which shows high levels of HER-2 in dark brown. As these cells grow very quickly doctors know that HER-2 positive tumours need rapid treatment.
Treatment: Researchers designed a drug (Herceptin) which detects cancer cells with abnormally high levels of HER-2. Herceptin is an antibody which specifically binds to HER-2 proteins and tells the immune system that the cell needs to be destroyed. Therefore the identification of HER-2 as a biomarker for a type of breast cancer has resulted in quicker and more effective treatment for HER-2 positive breast cancer patients.
Video of Herceptin in action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=66z6BmeA00I
More about biomarkers http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biomarker_(medicine)
Discussion Points: When would detecting biomarkers be useful? Do we need a biomarker for every health issue? Why are antibodies often used to detect protein biomarkers? Biomarkers aren’t always proteins. What else could be a biomarker? How could they be measured?
