I am sure you spotted that the photograph above is a photoshopped fake, but according to a recent study at Warwick University, about a third of manipulated images go undetected by viewers.
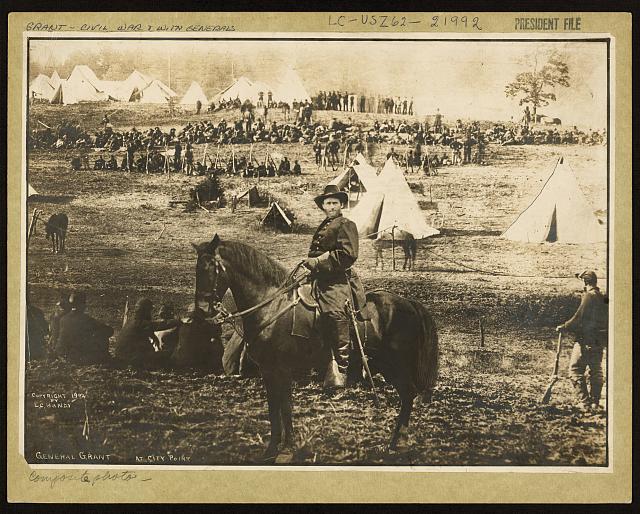
Physical manipulation of images has been around since the invention of photography itself. Take a look at this example from the early 20th Century; it looks convincing but the Library of Congress were able to work out that this is actually a composite of several images and does not really show General Ulysses S. Grant at City Point:

Modern digital technology has brought with it a plethora of photograph and video editing apps that are easily accessible and simple to use – at the touch of a button we are now able to crop, edit and filter the photographs we take. While fun to use for entertainment and valuable for people such as designers and artists, tools such as these can be more problematic when they are used with the intention to deceive or manipulate.
For example, in March 2018 a photograph from Teen Vogue of Emma González, an American anti-gun activist, was photoshopped to show her tearing up the US Constitution with the presumed aim of promoting her views as unpatriotic:
Out of Context
Manipulated images are not the only problem. Purposefully using a picture out of context can also mislead the intended audience.
In April 1934 a number of American newspapers, including the highly respected New York Times, published a photograph showing a man using a flying machine that worked using his lung power alone. The incredible image depicts a man in mid-air wearing a device consisting of a box and two rotors while four other men run along below him. Unfortunately, the newspapers had failed to check the original source of the image and fell afoul of a German magazine’s April fool’s joke.
While publishing a fake flying machine might be a fairly harmless, if embarrassing, mistake some images taken out of context like this can have more powerful consequences.
In July 2018 Time magazine used the cropped image of a young girl crying juxtaposed against a stern looking President Trump on their front page; the child was said to have been separated from her parents as part of Trump’s zero tolerance policy toward those crossing the border illegally from Mexico. The original photograph, taken by Getty photographer John Moore, went viral, sparking a public outrage that led to the government ending the practice. However, it was discovered that, on this occasion, the child had not been separated from her parents but was detained with her mother.
Both of these examples, highlight the importance of checking the source and confirming the context of an image before taking it at face value.
This can be true of videos too, take this example purporting to show U.S. President Donald Trump removing his hat and revealing that he’s bald:
https://twitter.com/PaulLeeTicks/status/1105227741484376064
You can see toward the end of the video, a slight glitch where the President’s hand seems to go through the top of his head, showing it to be an obvious fake but even if this wasn’t clear, the origin of the video would provide another hint that it’s not to be trusted – the video was created by Paul Lee Ticks, a Twitter user who frequently posts memes and digitally manipulated videos.
While some images and videos are obviously fake others can be more convincing and improvements in technology, particularly artificial intelligence, are making the fakes even more difficult to detect. These more convincing images and videos are known as deepfakes and with the ability to make people appear to say things that they did not, they have the potential to cause serious damage.
Take a look at this TED talk by computer scientist Supasorn Suwajanakorn, who explains his work with AI and discusses both the creative and more negative ethical implications of the technology:
Spotting the Fakes
With the creation of fake images and videos proliferating in journalism, politics and social media, it’s increasingly important to be vigilant. While experts are developing tools to help fight against the more serious attempts at disinformation, we have some simple tricks you can use to help improve your fake image savvy too:
Top Three Ways to Spot a Fake
-
Look for inconsistencies
Check the image for distorted backgrounds, missing or altered reflections and shadows, and missing features that you would expect to see. Keep an eye out for any obviously repeated patterns and be wary of lower quality or blurred images.
-
Try a reverse image search
Use a reverse image search on Google to track the image, see if it has been circulated before, locate the original source or maybe even find if the story around the image has already been debunked.
-
Check the metadata
Sometimes it is possible to look at an image’s metadata, that is, data about the image such as what time and date it was taken, which camera was used and if it has been saved in Photoshop. This is called the EXIF data. There are various websites and apps where you can upload an image to check it’s metadata but it’s simple to find out some key information using Windows too: right click on an image, go to properties then details. Unfortunately, not all images will have metadata as some popular sites such as Facebook and Twitter will remove it to protect user privacy.
Now you’re armed with these top tips why not take a look at the test the University of Warwick used in the study mentioned at the beginning of the blog. How many fakes can you spot?
Sources:
Boese, A. (no date) Man Flies By Own Lung Power. Available at: http://hoaxes.org/af_database/permalink/man_flies_by_own_lung_power (Accessed: 22 March 2019)
Brightside (no date) 10 Tips to Spot a Fake Image and Not Let Photoshoppers Fool You. Available at: https://brightside.me/wonder-curiosities/10-tips-to-spot-a-fake-image-and-not-let-photoshoppers-fool-you-469660/ (Accessed 22 March 2019)
Evon, D. (2019) ‘Is This a Video of President Trump Without His Toupee?’, Snopes, 12 March. Available at: https://www.snopes.com/fact-check/trump-toupee-video-fake/ (Accessed 22 March 2019)
Farid, H. (2019)’Don’t be fooled by fake images and videos online’, The Conversation, 20 February. Available at: https://theconversation.com/dont-be-fooled-by-fake-images-and-videos-online-111873 (Accessed 25 March 2019)
Kirby, J. (2018 ) ‘Time’s crying girl photo controversy, explained’, Vox, 22 June. Available at: https://www.vox.com/policy-and-politics/2018/6/22/17494688/time-magazine-cover-crying-girl-photo-controversy-family-separation (Accessed: 22 March 2019)
Library of Congress (2008) Civil War Glass Negatives and Related Prints. Available at: http://www.loc.gov/pictures/collection/cwp/mystery.html (Accessed: 22 March 2019)
Mikkelson, D (2018) ‘Was Emma González Filmed Ripping Up the U.S. Constitution?’, Snopes, 25 March. Available at: https://www.snopes.com/fact-check/emma-gonzalez-ripping-up-constitution/ (Accessed 22 March 2019)
O’Sullivan, D. (2019) ‘When seeing is no longer believing: Inside the Pentagon’s race against deepfake videos’, CNN Business, no date. Available at: https://edition.cnn.com/interactive/2019/01/business/pentagons-race-against-deepfakes/ (Accessed: 22 March 2019)
Smith, B. (2018) ‘Fake news, hoax images: How to spot a digitally altered photo from the real deal’, ABC News, 24 July. Available at: https://www.abc.net.au/news/science/2018-02-11/fake-news-hoax-images-digitally-altered-photos-photoshop/9405776 (Accessed: 25 March 2019)
TED (2018) Fake videos of real people — and how to spot them | Supasorn Suwajanakorn. Available at: https://youtu.be/o2DDU4g0PRo (Accessed 28 March 2019)
University of Warwick (2017) One third of fake images go undetected in recent study [Press release] 18 July. Available at: https://warwick.ac.uk/newsandevents/pressreleases/one_third_of/ (Accessed: 22 March 2019)
Vick, K. (2018) ‘A Reckoning After Trump’s Border Separation Policy: What Kind of Country Are We?’ The Times, 21 June. Available at: http://time.com/5318229/donald-trump-border-separation-policy/ (Accessed: 22 March 2019)





 You already know that referencing is important – it not only gives credit to the original creator of a work you have used but also helps to highlight your skills as a researcher; showing that you have read around your topic, found relevant information, applied it to your arguments and used it to develop your own ideas.
You already know that referencing is important – it not only gives credit to the original creator of a work you have used but also helps to highlight your skills as a researcher; showing that you have read around your topic, found relevant information, applied it to your arguments and used it to develop your own ideas.