


Intangible and Digital Heritage Consultant
The National Trust looks after one of the world’s largest and most significant collections of art and heritage objects set within their historic context. As ideas around heritage change enveloping not only the tangible but intangible heritage. We realise our duty of care extends beyond objects to the non-physical heritage such as folklore, traditions, and language that make our sights so unique. In addition we recognise the increasing amount of born digital material that will one day become the heritage of the future. We are therefore looking for a person to help us collect, manage, and curate the intangible and digital heritage of our sites in the region.
We expect this person to be experienced in collecting, managing and curating intangible heritage such as oral histories and be confident in their digital skills.
What it’s like to work here
The National Trust Consultancy is home to specialists in every field of our work. It’s a place where resources are shared across disciplines and boundaries, and it’s a great repository of skills, talent and experience. The diversity and quality of expertise within the Consultancy enable our properties and places to benefit from creative and innovative thinking, as well as deep expertise in all matters relating to our twin purpose of caring for the nation’s heritage and landscapes and making these accessible to all. The Intangible and Digital Heritage Consultant role sits within the Consultancy.
What you’ll be doing
You will be advising sites on their collecting and managing of intangible and digital heritage, supporting them during their intangible heritage projects and organising the collection of object metadata for surrogate collections. You will work between regional IT and the sites to ensure the needs of sites are considered, while simultaneously ensuring IT is able to keep a secure and stable digital infrastructure. You will also manage relationships with third party archives, to help guarantee access to material for staff and volunteers.
You will also provide tactical and strategic advice to the sites on how move modern opperation files to the archive, while also ensuring sites adhere to the National Trust policies around climate friendly storage.
Who we’re looking for
Update meeting on Intangible and Digital heritage at Seaton Delaval Hall
26/09/2028
13:00
Seaton Delaval Hall
Participants
General Manager
Regional Curator
Project Lead
Intangible and Digital Heritage Consultant
Agenda
Introduction
Status Update
Discussion Topic 1: Dialect dictionary
Discussion Topic 2: Auction Items
Decision 1: Film Archive
Agenda for next meeting
Summary
Everything is ready to go with Storyland. Three institutional oral history recordings taken. Student project for a dialect dictionary is on track. Possibly will lose out on Garden Painting at Auction but metadata collected. Need to revisit somethings in Film Archive arrangement.
Decisions
| Decision | Notes |
| Dialect Dictionary Illustrator | Using the illustrator Rainham |
| Donating (some) items to Film Archive | Definitely happy to donate some material but unsure about some footage take by volunteer. |
Actions
| Action | Person | Deadline |
| Contact students for Oral History interview | Project Lead | Within the next three months |
| Check with interviewer of gardening volunteer if they think another interview is required | General Manager | As soon as possible |
| Send extra tickets to storyteller | Project Lead | By the end of the week |
| Talk to volunteer about archiving film footage | General Manager | Before meeting with film archive |
| Arrange another meeting with film archive | Intangible and Digital Heritage Consultant | Within a month |
// “To invent the sailing ship or steamer is to invent the the shipwreck. To invent the train is to invent the rail accident of derailment. To invent the family automobile is to produce the pile-up on the highway.” (Virilio, P. (2007) The Original Accident. Cambridge: Polity, p. 10)
// To have an interactive game in your museum is invent the “out of order” sign and
// to open a heritage site is to invent the tape which communicates “sorry this part of the house is closed due to restoration”.
// Any creation brings with it everything that could possibly go wrong and also all the things that need to be done ensure things do not go wrong.
// This includes a curated visitor experience on a heritage site. Many things can go wrong, so there are a lot of things to do to ensure things run smoothly: are there enough volunteers to show visitors around, are the toilets clean, is the cafe well stocked, is the art collection available to view, are the gutters clean so they do not flood in case it rains. And for National Trust sites there is added pressure because the visitor experience also needs adhere with the expectations people have of National Trust sites.
// The theme of this conference is ‘experience’ and I would like to talk about
// the labour necessary to allow an experience to be experienced on a heritage site
// specifically the maintenance labour, and how
// maintenance labour’s position in society radically influences the running of heritage sites and
// how this effects the work I am doing with my PhD which is in collaboration with the National Trust property Seaton Delaval Hall.
// I think we need to start by understanding what maintenance labour is
// I am going to do by introducing you to three characters with three stories that will help me illustrate the nature of maintenance work and the position it holds in society: Jo, who is part of my supervisory team, the collector and entrepreneur Robert Beerbohm, and the artist Meirle Laderman Ukeles.
// Jo works for the National Trust as a curator among other things, titles are a bit vague in the Trust so I am not completely clear on what they do, this is also not a picture of them, obviously. They told me a story of when they were walking around a Trust property together with their predecessor. Their predecessor decided to point out some of their biggest achievements, which was not a new cafe or an exhibition but
// a window frame that look exactly like it did when they started. This is a perfect embodiment of maintenance work, because if the predecessor had not pointed the window frame out to Jo, they admitted that they probably would not have noticed it at all. In this window there is no evidence of the predecessor work, their work is completely invisible which is common for maintenance work.
// We just expect our streets to not be full of rubbish, the toilets in our buildings to be clean, fresh water to come out of our taps. We often do not see, or wish not to see the effort behind these things.
// So they live an invisible life until things go wrong,
// which brings me Robert Beerbohm.
In the book How Buildings Learn Stewart Brand tells the story of the collector Robert Beerbohm, who had over million dollars’ worth of comic books and baseball cards stored in
// a warehouse in California. The roof had a known drainage problem but the building owners had not prioritised this to be fixed. One day there was particular heavy rain fall and the roof leaked terribly flooding the entire warehouse, damaging all the collectables. Beerbohm lost everything.
// If we compare the warehouse to the window in the Trust property, we see how maintenance only becomes visible once it has failed or not been done at all. The window was maintained but there are no traces of the work put in, while the warehouse was not maintained and the results are obvious and catastrophic. Maintenance only becomes visible in a negative way.
// As Brand says maintenance work is “all about the negative, never about rewards.” If the roof had been fixed and the roof did not collapse Beerbohm would not have technically gain anything but he also would not have lost anything either. He would however not be aware of the lack of loss because nothing happened. All maintenance offers is stability, no tangible reward, in fact Beerbohm would have lost money on fixing the roof and that is exactly how it would have felt, as a loss. Maintenance always feels like a loss and a waste because it takes time, work and money to do it and in the end you have nothing new to show for it. You just go back to where you started. You keep the window frame exactly the way it is. And then once it is done you have to start all over again.
// And yet as Brand concludes “the issue is core and absolute: no maintenance, no building.”
// The artist Mierle Laderman Ukeles,
// wrote a manifesto titled
// Manifesto for Maintenance Art 1969! And in it Ukeles presents this idea of society dividing up labour into two systems:
// the development system and the maintenance system. The words Ukeles uses to describe the maintenance system
// “Keep the dust off, preserve, sustain, protect, defend, prolong, renew” all fit within the tales of Jo and Beerbohm, maintenance is about protecting, prolonging and generally keeping the dust off things. But it is how Ukeles describes the development system that really puts things into perspective:
// “pure individual creation; the new; change; progress; advance; excitement”. These are some really fun buzzwords. You are going to want to get some of these into your funding application.
// And that is exactly what Ukeles is trying to tell us with her manifesto, in society we value development over maintenance. When child comes home from school they want to talk about their fabulous new sculpture made from a milk carton sellotaped to piece of cardboard with stuck on googly eyes.They are not going to tell you about how they tidied up the classroom after they had finished crafting their masterpiece to make it look exactly like it was before they got out the scissors and glue. We do not care about maintenance. Maintenance is less fun, as
// Ukeles says “Maintenance is a drag; it takes all the f***ing time”. And because we do not care for maintenance work means that we do not reward people for maintenance work.
// In her art Ukeles discusses the unpaid domestic labour she has to do as a mother but also the labour carried out by the sewage department for example, which is also not going to make you the big bucks.
// To quickly summarise,
// maintenance is often completely invisible because the outcome makes things seem to ‘stay the same’,
// it is deeply undervalued in society due our obsession with development,
// and yet it is utterly essential. This is the case everywhere and
//heritage sites are no exception.
If you work on a heritage site two of the hottest topics of conversation is not what the soup of the day is but
// volunteers and funding and both are severely affected by our societies rather negative view of maintenance work.
To start with let’s look at volunteers.
// Just like we rely on maintenance workers to remove the rubbish from our streets, fix our pipes, and clean our nappies, we all rely on
// National Trust sites to look like National Trust sites, if they don’t we get angry. Let’s take a more specific example –
// a National Trust garden. A National Trust garden has a look, it is essential that it gets achieved every year for visitor satisfaction, which means it often is achieved every year.
// So we are kind of going back to the window. Every year the garden looks the same, just like the window, and this stability erases the traces of labour giving the illusion of a magical garden that always looks this great. But this does not just happen.
// It requires a lot of work and who does this work?
// A couple of head gardeners (a classic maintenance job)
// and mostly, because it is the National Trust, volunteers, literally people who do not get paid to do the work.
// Now volunteering is a fantastic opportunity for people to build a community and keep themselves generally occupied, I cannot deny that. But you can also not deny that a volunteer doing gardening is putting a professional gardener out of a job.
// In the paper Making usable pasts: Collaboration, labour and activism in the archive, an archivist, Carole McCallum, from Glasgow Caledonian University (GCU) is quoted saying that she did not want bring volunteers into the archive because it would put a professional out of a job.
// In another paper on ‘punk archaeology’ the author writes “If people are willing to undertake some forms of archaeological work for free, it is possible this will impact on the value of paid work in the sector.”
// The use of volunteers on heritage sites creates a vicious cycle, it starts with
// maintenance labour being undervalued,
// maintenance jobs then are the first to become unpaid volunteering opportunities, and
// because the work is now done for free the value of the maintenance work drops again because who would paid someone to do a job when another does it for free.
// Moving on to funding. It is common knowledge that heritage sites like the majority of organisations in the culture sector rely on money from big funding bodies.
// Funding bodies therefore have a lot of decision power over what gets money and what does not. If you go to the National Lottery Heritage Fund website and go to the “Projects we’ve funded page” and type ‘develop’ into the search bar you get two pages of results. Now this is not a lot but that is because it just searches titles.
// Nevertheless if you type in maintenance you get one hit. This is no the most solid evidence and I am looking to do audit of the types of projects that have been funded by large funding bodies. But for now it will have to do, it hints at a difference in value. However, there is one other thing, in this single maintenance hit the title includes the term restoration. It is important to point out that restoration and maintenance are not the same thing.
// In How Buildings Learn Stuart Brand quotes John Ruskin, “Take proper care of your monuments, and you will not need to restore them. Watch an old building with an anxious care, guard as best you may, and at any cost, from every influence of dilapidation.” Restoration is only necessary when maintenance fails.
// Now if you type restoration into the search bar you get many pages of projects. The National Lottery Heritage Fund gives a lot of money to restoration projects. You see restoration and development deliver the same amount of satisfaction, the before and after is impactful and makes everyone go ‘ooh’ and the funding bodies can go home feeling that they made a difference. But if we follow Ruskin then they would not need to do this if they funded maintenance. But as we know it is not sexy and above all it is endless. You cannot fit maintenance into a time limited project and the way the funding systems works we have to work in terms of projects and tangible achievements, so funding maintenance is not an option.
// So to summarise our undervaluing of maintenance in society has led to
// an increase in volunteers replacing paid jobs and
// funding bodies to focus on development and restoration above maintenance projects. And this is where we get to the real painful part, because this is not going to change. We live in an extreme capitalist society which has not changed much since
// Ukeles pointed out how we do not about care about maintenance work more than fifty years. Look at how we treat our key workers. We clapped for them for a bit
// but now the vacancies in care and hospitals speak for themselves and you cannot avoid signs asking you not to abuse the staff in most place’s where key workers operate.
// So society is not going to change but I still have to finish my PhD by 2025 so I will have to work within this framework.
// My project is specifically looking at how to sustain (re)use of oral history recordings on heritage sites and I am working in collaboration with Seaton Delaval Hall. So basically I am designing a type of archive because currently archives are not oral history recordings’ best friend.
// What I am doing is 100% part of
// the development system, and my collaboration partners, the staff at Seaton Delaval Hall are the
// maintenance workers who have to keep the dust off my creation. Now of course they could simply
// throw my work into the bin after January 2025 but for my own sense of pride I would like to avoid that. I believe this means I must understand and incorporate ideas of maintenance into my work.
// First thing I need to do is make something
// realistic. Now that sounds obvious but currently people are very obsessed with getting technological solutions to problems,
// which is great but not very realistic.
// Not a lot of people have the capacity to maintain super complicated digital softwares and considering the National Trust’s reliance on volunteers, who unlikely to have significant computer coding skills, they do not have the labour capacity to handle the maintenance of certain technological solutions. I also need to be realistic when it comes to
// the time and money people are able to dedicate to maintaining my design. Understanding where my work can fit into the day-to-day running of the Hall is crucial otherwise it is likely to constantly be put on the back burner until there finally is a ‘good time’ to work on it, which given the pressures on the staff is unlikely to be a regular occurrence.
// The second thing I need to do is make it adaptable.
// Things change all the time and before you know it you are in a global pandemic.
// Which is why I imagine a certain level of DIY needs to be part of my work,
// allowing the maintainers of my design to adapt it to their current needs rather than having to bend to my old requirements.
// Currently I hope that by doing a placement at the Hall I will be able to better understand the needs and desires of those who will be keeping the dust off my work and then be able to make something that fits into the maintenance system at the hall instead of imposing my development system onto them.
What follows is a summary of the various seminars that I took presented by Ian Biddle from Newcastle University. Overall I enjoyed these seminars mostly because I had covered many of the topics during my time at Goldsmiths but now I understand it better.
You can read many things as texts: buildings, art, music etc. The word text comes from the word to weave. A text therefore represents a complicated set of ideas woven together to create one idea.
There is a lot of snobbery and hierarchical thinking around text and the author. Author come from the word authority. However to say that the author has complete authority over a text is a very outdated idea. Everyone interprets and experiences texts in a different way. This is often due to the various elements that make up their background: gender, race, work, economical background etc. In addition to this snobbery around interpretation there is also the also now outdated belief that cultures that have no text, have not published, have no history. Which is a bit racist.
I wrote a summary in a blog post

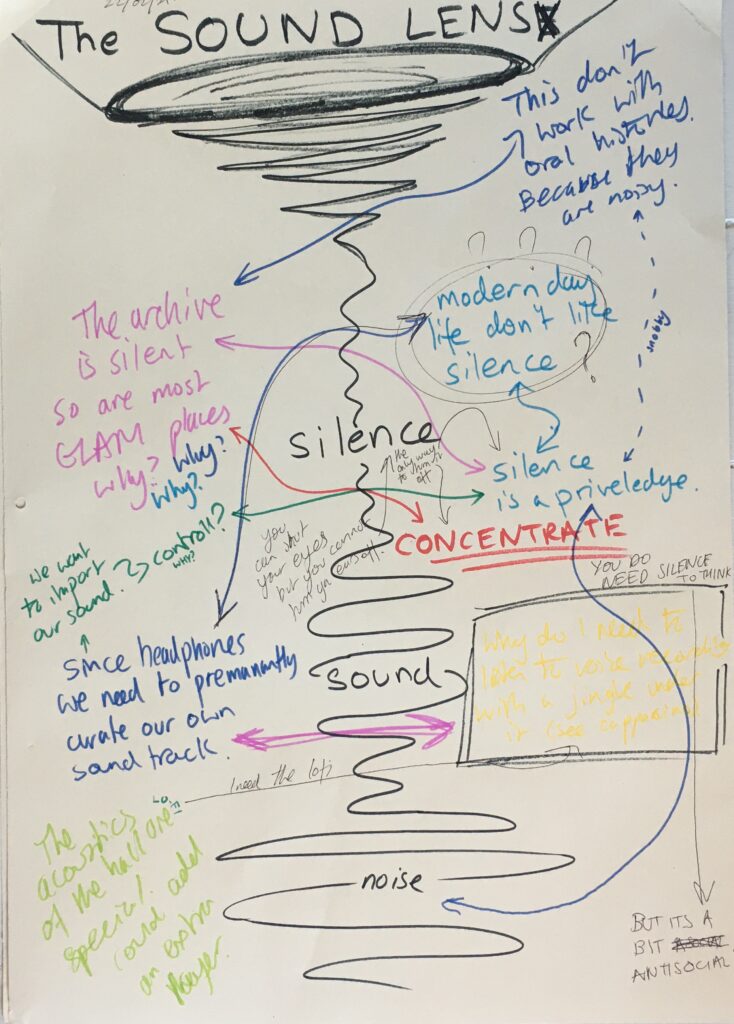
Sound is married and dependant on technology. They way we experience sounds has developed in correlation with tech look at the invention of noise canceling headphones but also the noise of industry and cars that infiltrates our everyday surroundings. Because of advancements in speakers listening has become a contact sense. We can now feel the beat of the music move our bones to the rhythm.
There is a spectrum of sound where music is on one end and noise is on the other. Where sounds fall on this spectrum changes with time and whoever is listening.
How we perceive sound and our experience of it has changed dramatically over time. We now live in a world of lo-fi sound, a constant blurry noise where we cannot make out the specific sources. Before we live in hi-fi sound. Everything could be heard crystal clear because we did not have the rumble of the machines.
Our relationship with silence is also very strange. Sound proof housing in a city centre is extremely expensive. To have access to silence is a privilege. Yet we are also afraid of silence. We are constantly turning on music and TV. Most people cannot walk from A to B without having headphones in. I think we have a need to control our sound.
Slavonic Languages have different words for listening but I haven’t been able to find any examples.
‘Acousmatic Sound’ listening to a sound without know the source. Basically Greek philosophers would stand behind a curtain and speak in an effort to get the audience to concentrate better on what they were saying.
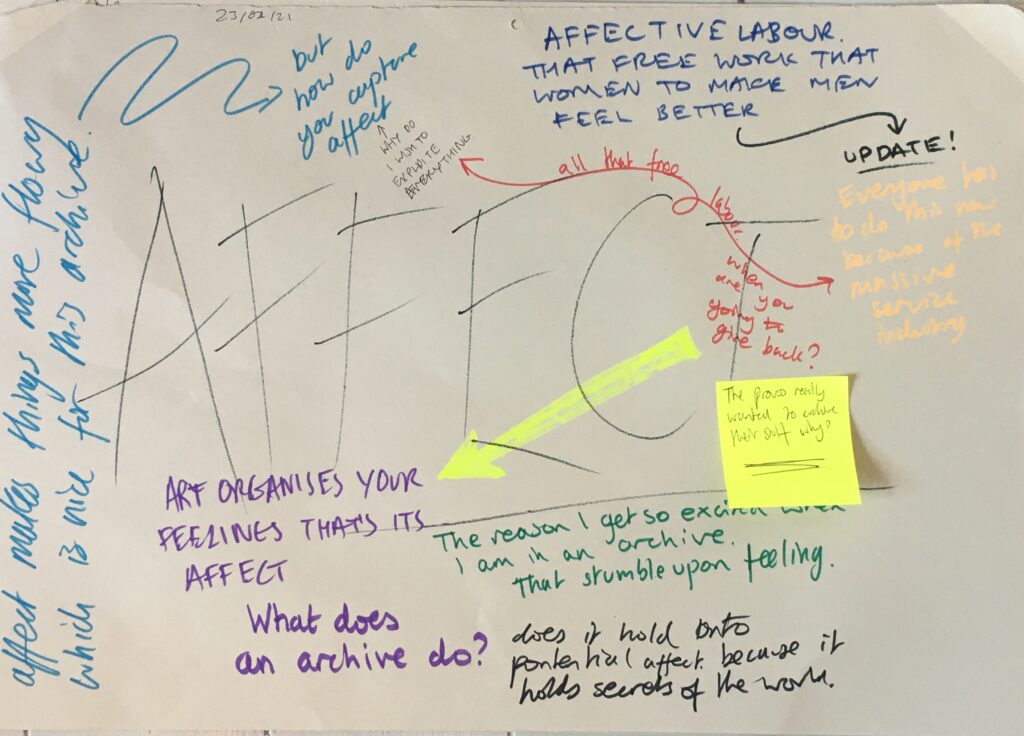
Affect (psychology) = mood
Affect (philosophy) = the grammar of emotions
Affect labour = labour that is conducted in the service industry often considered feminine work
Affective computing = instead of the old input output model this type of computing is focused on interface
Feeling works on a very different logic. It’s the body of knowledge outside of the rational that controls emotions. It is in a sense a different world that we live in.
Affect. Complicated political thinking without attracting too much attention or a specific type of attention from a suppressive state. Think Provo and their ludike actions.
Art organises your feelings. It’s that ah! moment when you see a work of art that perfectly communicates a complex feelings.
Affect theory kills boundaries. Biddle’s tip if you are stuck throw some affect theory at it. It’s not political and it unpicks the logic of other theories.
This is an easier version of Derrida.
To make an archive is to repeat. It is a deeply nostalgic act with questionable productivity. “I just want to relive it”
The archive represents the now of whatever kind of power is being exercised anywhere at any place or time.
There is a feverish desire – a kind of sickness unto death – that Derrida indicated, for the archive: the fever not so much to enter it and use it, as to have it, or just for it to be there, in the first place.
Stedman, Dust
We have to have all the data.
And currently those who are in power (big tech) are also mining all the data for reasons no one is completely sure about less of all them.
Archives are full of metaphors. From the architecture of the buildings that store them to the icons we use to store data on our laptop. This is common theme in new technologies. The first cars looks like carriages and the save button is a floppy disc. However some of these metaphors are more tailored to the elite, as in the elite are more likely to recognise this metaphor or the metaphor represents an elite version. Just look at the representation of the Jedi library in Star Wars it is nearly exactly the same as the library at Trinity College in Dublin. Why would Jedis need books?


The putting something in an archive is called archivisation. By archiving something you move it from the private into the public but not from the secret to the non-secret. That is because archives promise access but do not always give it. An archive can be compared to house arrest, the documents are not in prison but they are also not free.
Archives are particular anxious places. They worry a lot about the longevity of their collections and general rot. There is also the added anxiety that new forms of preservation leads to new forms of loss. When we were able to record sound we had to learn how to archive it. I cannot imagine the amount of loss that is created by the internet.
Quick warning here to not fetishise the archive please.
