Exhibition now open to the public March – August 2017.
Level 1, Philip Robinson Library, Newcastle University.
The text and images below are from the exhibition, ‘Cataloguing the Collector: The life and career of Frederick Charles Pybus’. Items within this exhibition are taken from the Frederick Charles Pybus Archive.
Exhibition talk: ‘The Life of the Collector: Frederick Charles Pybus
ALL WELCOME
Date: 29th March 2017
Time: 5.30-7pm
Location: Room 152, Level 1 of the Philip Robinson Library
A talk on the exhibition will be given by our archivist Alex Healey hosted by the Friends of the University Library.
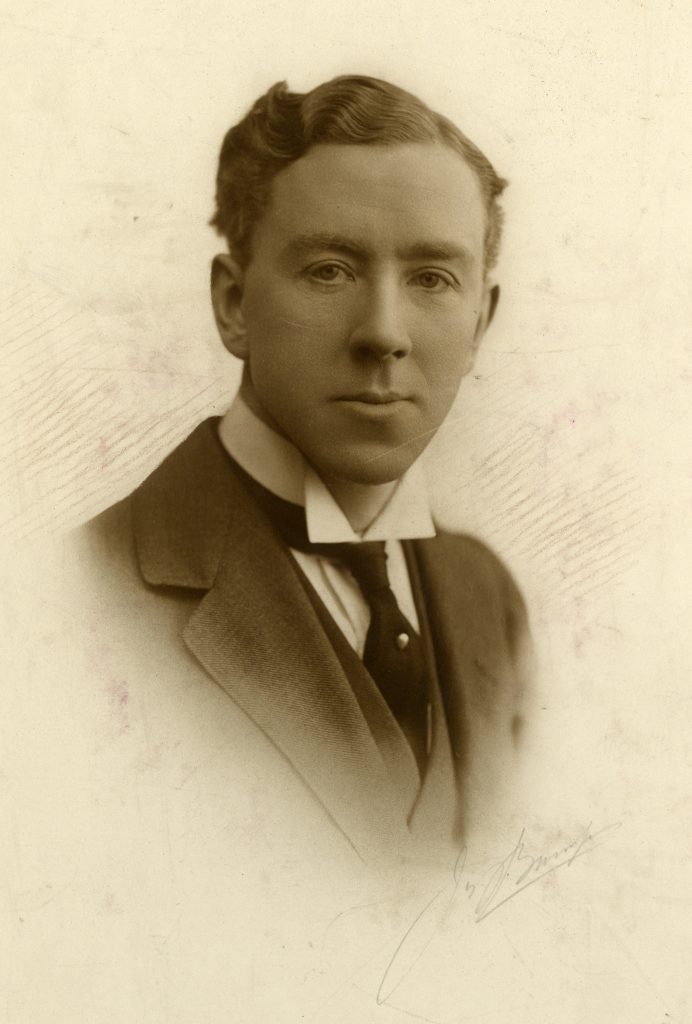
Frederick Charles Pybus is arguably best known for his collection of historic medical books, held here in the library. However, items from his personal archive reflect his medical career and personal interests, demonstrating that collecting was only one aspect of his personality.
Pybus the Surgeon
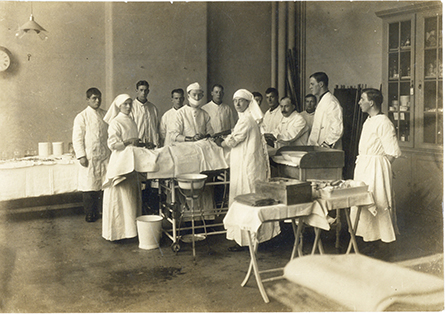
Surgery team including Pybus ready for theatre in the Fine Arts department at Armstrong College, 1st Northern General Hospital, c. 1915 (Professor Frederick Pybus Archive, FP/1/3/9)
At the start of the 20th century, medical developments relating to antiseptics and anaesthesia allowed surgeons to perform more elaborate and lengthy procedures on their patients.
Frederick Charles Pybus entered the profession, registering as a medical student in 1901 and graduating in 1906. He was to remain associated with the medical profession for over 50 years, until his retirement in 1961.
Pybus not only witnessed the development of surgery in this period, but himself conceived and undertook experimental processes on his patients, contributing directly to the development and improvement of surgical procedures, including tonsillectomies and the removal of cysts.
With the exception of a brief stint in London after his graduation, Pybus’ career both as a student and a practitioner was spent working in medical institutions here in Newcastle, including the Royal Victoria Infirmary, the Fleming Hospital for Sick Children and the Newcastle General Hospital.
Pybus the Veteran
The Royal Army Medical Corps (RAMC) were responsible for the wellbeing of all military personnel during the First World War. As well as serving overseas, members of the RAMC worked on the home front. Suitable buildings were requisitioned as hospitals to accommodate the huge number of wounded soldiers returning from the trenches.
Pybus received his papers placing him on reserve duty in 1910. When war arrived four years later, he helped requisition Newcastle University’s Armstrong College for use as the 1st Northern General Hospital.
Over 1000 operations were performed by Pybus at the 1st Northern, at least some of which were performed in what had been the Fine Arts department. Many surgeries were attempts to correct the damage caused by gun-shot wounds and it was during this period that the field of plastic surgery was developed.
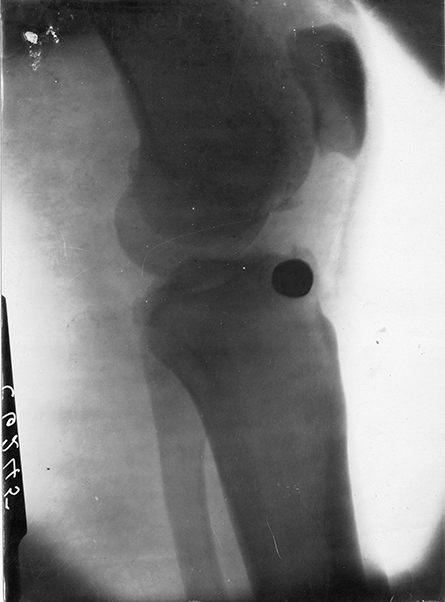
Image included in patient notes for removal of a bullet from Private J. Shrubb of the Inneskilling Fusiliers, Sept 1914 (Professor Frederick Pybus Archive, FP/1/3/3)
Pybus and Children’s Medicine
After the First World War Pybus was appointed Assistant Surgeon at the Fleming Memorial Hospital for Sick Children, located at what is now Princess Mary Court in Jesmond.
The early 20th century was a period of change for children’s hospitals, in which their status was shifting from being seen as the last resort of impoverished families, to places in which modern medical techniques, tailored to the needs of children, were delivered by skilled practitioners.
During this period, Pybus’ publications and research interests became focussed on the treatment of children. This culminated in the publication of his book The Surgical Diseases of Children: A Handbook for students and practitioners in 1922. The book was published in England and North America, and was received favourably by the medical press.

The Surgical Diseases of Children: a handbook for students and practitioners, 1922 (Pybus J.I.11)
Pybus and Cancer Research
At the start of the 20th century improved understandings of the causes of cancer caused this long known illness to become a focus of public debate. The understanding that environmental factors could directly cause cancer made the illness a social issue as well as a medical one.
As a result of this, research into the identification of carcinogens became increasingly popular as the 20th century progressed. Having spent some time at cancer specialist hospitals early in his career, Pybus established a Cancer Research Institute in Newcastle in 1925.
The Institute used animal testing to research bone tumours and was one of the first to suggest that atmospheric pollution could be a major contributing cause.
Pybus the Collector
Arguably, Pybus’ most well-known legacy is the Pybus Collection of historic and rare medical texts. He became interested in such books after an encounter with a ‘really handsome book’ at the first meeting of the Association of Surgeons in the early 1920s. He later recalled that this encounter with the ‘magnificent’ plates of a Vesalius folio ‘wetted his appetite with a vengeance’.
Despite offers from book dealers and American universities to purchase parts of the collection, Pybus donated it in its entirety to Newcastle University Library in 1965, where a dedicated reading room was established in the old library. The collection is now held by Special Collections here in the Philip Robinson Library, and is included on the library catalogue.
Pybus the Person
Much of Pybus’ life was taken up with his medical career and hobby of collecting medical texts. His archive demonstrates that these were the dominating aspects of his life. Nevertheless, there is evidence of other interests.
Other items in the archive hint at Pybus’ other interests. These include involvement with lecture societies, membership of Masonic organisations and an attempt to resurrect the historic Company of Barber Surgeons and Tallow Chandlers of Newcastle upon Tyne.
Other Resources
Interested in Pybus’ book collection. Find out more about the Professor Frederick Pybus Collection.
More about Pybus our blog: