Update: Author manuscript available
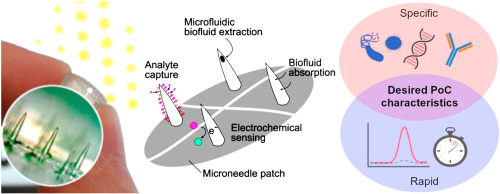
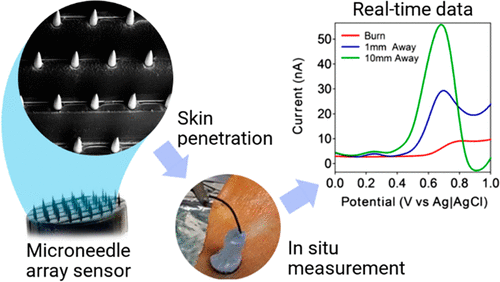
One of the challenges in developing microneedle devices to capture disease biomarkers from the skin is the lack of suitable skin specimens in which to test the devices. Donor skin specimens that carry the specific target diseases simply do not come by easily.
I first discussed this challenge with Eirini Velliou, Tao Chen and Guoping Lian in April 2016. We decided to tackle it by growing our own model of diseased skin in the lab. Experimental work started shortly after, and continued to develop following my relocation to Newcastle University in 2017. Earlier this week, we described the collaborative work in a joint publication in the journal Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.
We took a grounds-up approach by growing melanoma skin cancer cells in a three-dimensional (3D) culture, supported structurally by a biocompatible polymer scaffold. This allowed us to simulate not only the biological microenvironment around the cells, but also the three-dimensional structure of the skin for microneedle insertion. Importantly, it was a simple and inexpensive, yet versatile, laboratory model to set up.
In pioneering the 3D cell culture model for evaluating microneedle devices against a skin cancer biomarker, we also demonstrated – for the first time – successful capture of S100B (a biomarker for melanoma skin cancer) in situ using our immunodiagnostic microneedle device.
Stella Totti, formerly a PhD student and now a postdoctoral researcher in Eirini’s research group, is the first author. I am especially pleased that hard work has paid off for Lorraine Dale, a former MSc student of mine, who contributed greatly to this work and is a co-author on this paper.
The paper is free to read until 28 July 2019 via this link: https://authors.elsevier.com/c/1ZBcy3IQMPEdJi