This Thursday, 7th August, is Cycle to Work Day, a national campaign founded by Cycling UK to encourage as many people as possible to commute by bike. Whether you are a regular rider or are considering cycling to work for the first time, it is a perfect opportunity to start! This blog outlines the benefits of cycling, Newcastle University’s support for cyclists, and relevant resources and events.
Benefits of Cycling
Cycling to work offers a wide range of benefits that impact health, finances, and the environment:
- Improved physical and mental health
- Cost savings on commuting
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Avoidance of traffic congestion with more predictable travel times
- Increased productivity and energy during the workday
- An enjoyable and active commute
For a more detailed overview of these advantages, see Cycling UK’s article: Six reasons you should cycle to work.

Newcastle University Facilities for Cyclists
The University supports active travel by providing secure bike storage, showers, and changing facilities to encourage cycling among staff and students. Information on these facilities are available on our cycling page.
Additional resources such as tips on bike storage, cleaning, and repairs are available in our Bike Maintenance Blog.
Staff and students can join the Bicycle Users Group (BUG) on Teams for updates and advice by emailing sustainable-campus@newcastle.ac.uk with the subject line “Join BUG.” We currently have over 460 members on the Teams channel!
The University also participates in the government-backed Cycle to Work Scheme, which enables staff to purchase bikes and safety equipment through salary sacrifice, resulting in significant cost savings. Check out an in-depth description and some handy resources about the scheme on the People Services website.
External Resources and Events
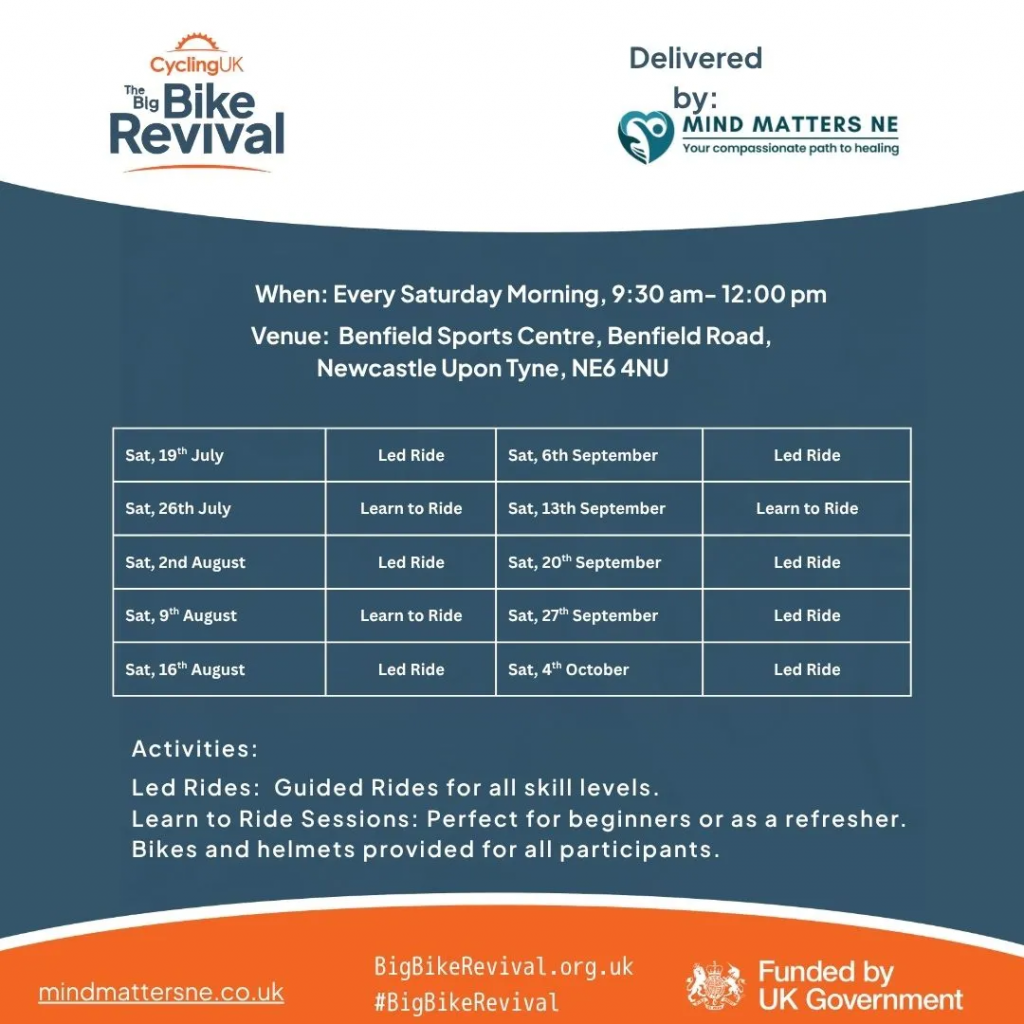
Beyond the University, there are excellent local opportunities to support and encourage cycling. Free confidence sessions are available through The Big Bike Revival, designed to help cyclists of all skill levels build road confidence and improve their skills. These sessions are open to anyone aged 18 and over. See below for dates, or see the website: The Big Bike Revival.
For those looking to plan their cycling routes, Cycling UK offers a handy Journey Planner tool, which helps identify the safest and most efficient paths for commuting by bike: Cycling UK Journey Planner.
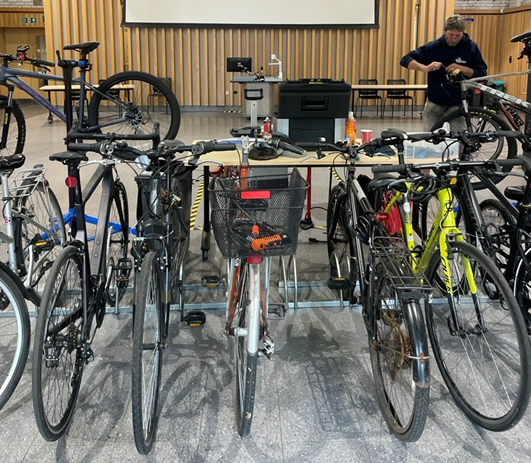
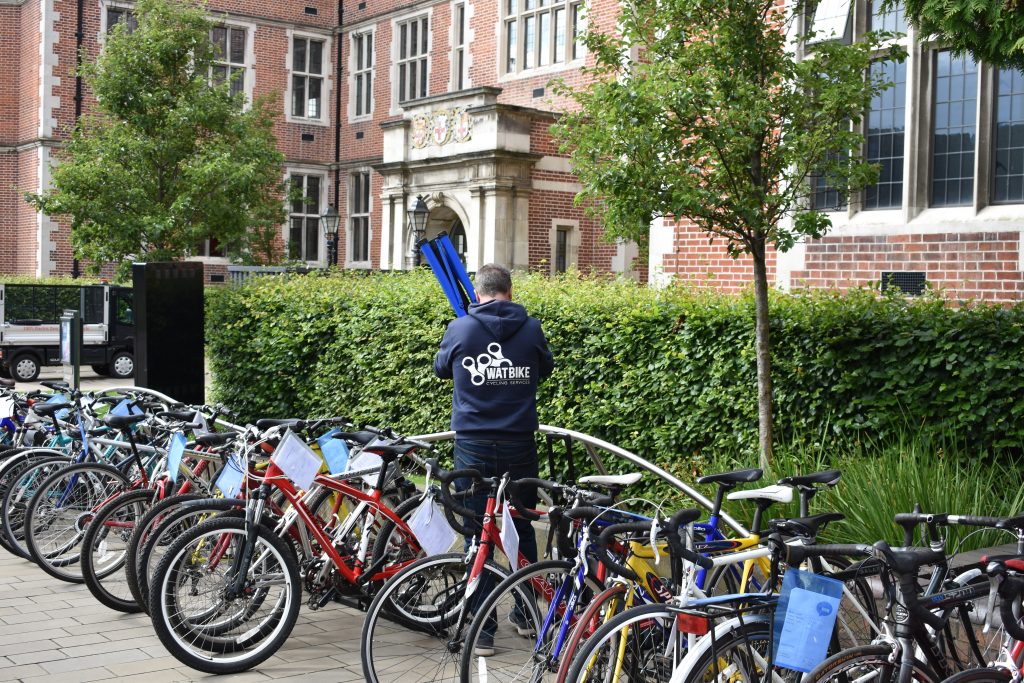
Dr Bike: Free Bike Maintenance Sessions
Dr Bike is a free bike maintenance service offered in collaboration with WATBike. These sessions provide minor repairs and comprehensive bike health checks (MOTs) to ensure bicycles are safe and ready for the road.
Since September 2024, a total of 25 Dr Bike sessions have been held across six different campus locations, with 424 bikes serviced so far. Additionally, two Bike Weeks have been organised alongside WATBike to promote cycling and bike maintenance awareness across the University community.
To coincide with Cycle to Work Day, a special Dr Bike session will take place at the Medical School. This session is open to all staff and students, but we recommend arriving early to secure a slot!
| Date | Location | Time | What3Words |
| Thursday 7th August | Medical School Reception Entrance | 10:00 am – 15:00 pm | count.rally.olive |
Tips for New Cyclists
If you’re considering starting your cycling journey, here are some essential tips to ensure safety and security:
- Always wear a helmet
- Obey traffic lights and road signals
- Don’t ride on the pavement unless a sign says you can
- Use lights and reflectors so you are clearly visible
- Don’t use headphones or a mobile while cycling
- Remove lights and accessories from your bicycle when it is parked
- Always securely lock your bicycle with at least one ‘Sold Secure’ certified cycle lock and only use purpose-designed Sheffield stands or racks
- Don’t leave your bicycle on campus overnight
- If possible, arrange adequate insurance to cover any theft or damage to your bicycle
- Join BUG to see if colleagues have any other helpful information for you or can supply information about recommended cycle routes
We hope this blog has given you some useful insights and inspired you to consider cycling as part of your daily routine. Happy Cycle to Work Day!