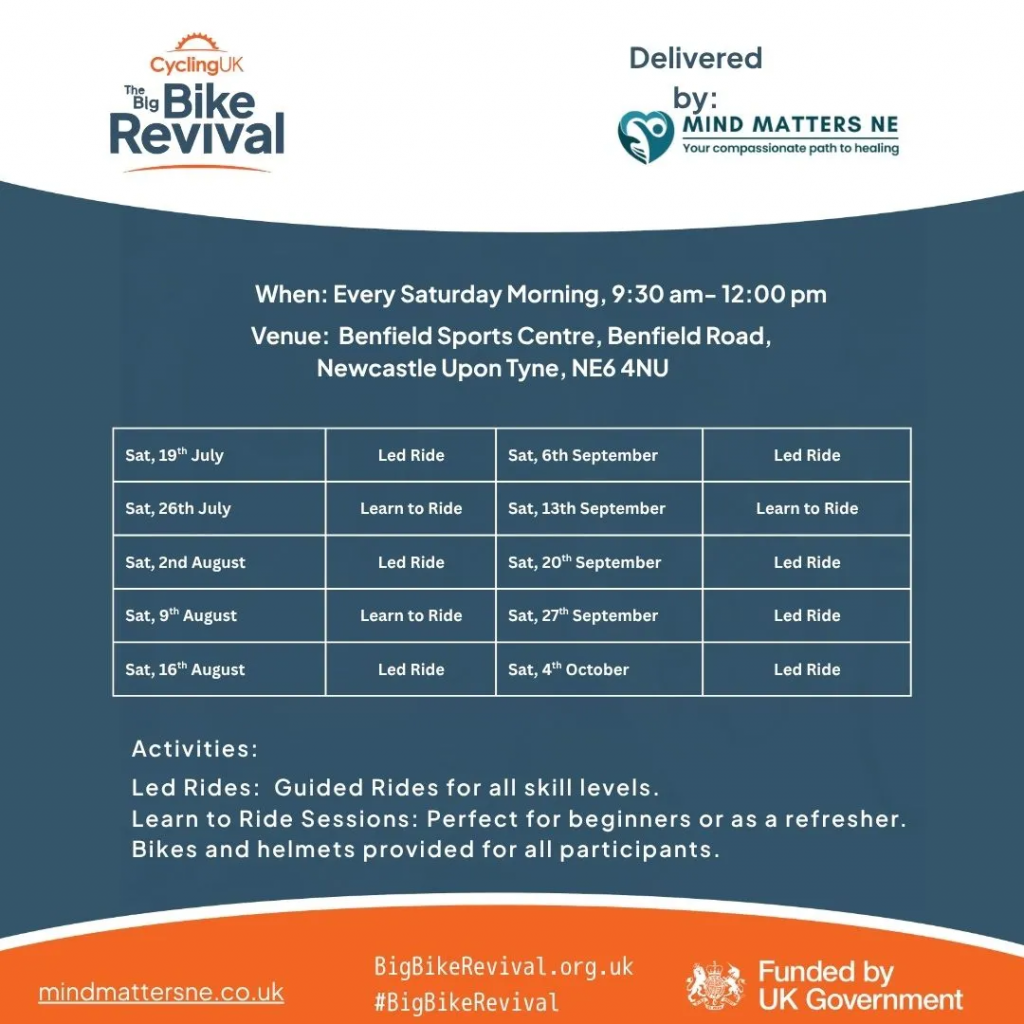
Fashion Revolution is an organisation that formed in 2013, following the Rana Plaza factory disaster. Since then, it has grown to become the world’s largest fashion activism movement, reaching over 80 countries worldwide. The movement challenges the fashion industry’s exploitative systems and pushes for a future that prioritises people and the planet. Through campaigns, education and community action, the movement helps people understand the issues in fashion and take steps to drive change.
Fashion Revolution Week is taking place from Tuesday 22nd April till Sunday 27th April 2025. This year, the theme is “Think globally and act locally,” encouraging us to reflect on how we can all play a part in transforming fashion, wherever we are. In this blog, we’ll explore what that looks like here in Newcastle – from local initiatives to simple everyday actions you can take to be part of the Fashion Revolution.
- Buy second-hand
Buying pre-loved items has become a growing trend amongst conscious consumers not just to save money, but as a way to resist fast fashion. By 2027, the global second-hand apparel market is expected to grow 3 times than the global apparel market overall (ThredUP, 2023). Second-hand shopping reduces waste, extends the life of clothing, and lowers your carbon footprint.
Here in Newcastle, the second-hand scene is thriving, with vintage shops, charity stores, and markets offering everything from upcycled hoodies to retro handbags. Some charity shop hotspots include:
- Clayton Street, Central Newcastle
- Gosforth High Street, Gosforth
- Whitley Bay High Street (if you fancy a trip on the Metro)
It is also worth checking out the following:
- Durham Vintage host a stall in the Quayside Market every Sunday, and host frequent warehouse sales
- Ginger’s Flea Market is an annual flea market held in the Boiler Shop. The event is taking place on Sunday 4th May.
- Vintage Vera is ran in the Newcastle Student Union Basement and contains endless racks of jumpers, jeans and t-shirts. Their next event is on Thursday 8th May.
- Green Heart Collective, based in Team Valley, stocks a vibrant mix of retro fashion and pieces made from sustainable fibres like bamboo and organic cotton. They also have refill stations and reuse packaging materials as part of their wider commitment to sustainability.
Shopping second-hand locally ties directly into this year’s theme of thinking globally and acting locally. When unsold clothing in the UK is shipped abroad – often to countries in the Global South – it can overwhelm local markets and contribute to growing textile waste dumps (WRAP, 2017). By supporting second-hand fashion here in Newcastle, we help slow down that cycle and reduce the burden on communities elsewhere.
- Repurpose older items
Another way to easily extend the life of a clothing item is by upcycling, tailoring or mending your existing items. There are many alteration businesses dotted around Newcastle, including StarStitch , located on Saville Row. From installing a new zipper, to mending tears, your favourite items will easily be revived for a fraction of their original price.
Alternatively, if you don’t feel like visiting a tailor, there are plenty of local groups designed to help you harness your DIY sewing skills. Here are a few ideas:
- The Baltic Sewing Bee takes place every Thursday, bringing together a network of keen sewers who can help you with any small sewing projects
- Hut on the Green is in Gosforth Central Park and teach sewing classes, as well as a range of other creative workshops
By repairing and reusing, we reduce our impact on the global fashion system while supporting skills and sustainability in our own community. For some easy and trendy upcycling tips, check out our other sustainable fashion blog.
Image: Nestled between the shrubbery of Gosforth Central Park, Hut on the Green, offers sewing classes for beginners (Source: Chronicle Live).
- Swap don’t shop
Clothing swaps are a fun, free, and sustainable way to refresh your wardrobe without buying anything new. By trading clothes you no longer wear for something new-to-you, you extend the life of garments and help reduce demand for fast fashion. There are a few swap points around Newcastle including:
- The People’s Exchange in Ouseburn allow you to “Shop, Swap or Drop” old garments. If you bring in a batch of items, you can earn a percentage of their resale value or receive store credit to spend on something new.
- Northumbria University have two upcoming swap shop events at their Student’s Union. The next even is taking place on Wednesday the 30th of April.
- The Magic Hat Cafe has recently held swap shops, usually on the weekend. Keep an eye on their page for any upcoming events!
Like upcycling and mending, clothing swaps keep clothes in circulation and out of landfill – a simple way to act locally while thinking globally. Plus, attending swap groups is a great way to connect with fellow fashion-lovers in your community.
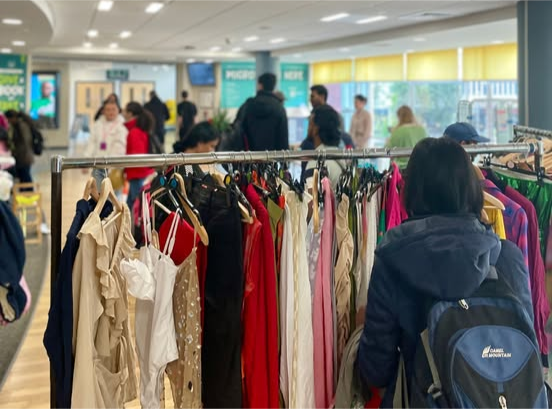
Image: A vibrant clothing rack on display at one of the many popular Swap Shop events hosted by Northumbria Students’ Union. (Source: Northumbria Students’ Union Facebook).
Fashion Revolution Week is a great time to remind ourselves of the meaningful action we can take right here in Newcastle. These small, local choices ripple outward, challenging the fast fashion system and reducing its impact on people and the planet. If everyone took up one of the three solutions mentioned above, we can reshape the fashion industry into one that values longevity over trend-chasing.
Thank you so much for reading! If you are interested in Fashion Revolution, you can subscribe to their newsletter here. For more information on what we do to be sustainable at Newcastle University, see our webpage or contact us at sustainable-campus@ncl.ac.uk
To learn more about the issues surrounding textile waste dumps, visit The OR Foundation; you can also explore the Speak Volumes campaign, which challenges global systems of waste colonialism, and the Clean Clothes Campaign, which advocates for the rights of fast fashion workers.
References:
https://www.wrap.ngo/sites/default/files/2020-10/WRAP-valuing-our-clothes-the-cost-of-uk-fashion_WRAP.pdf
https://cf-assets-tup.thredup.com/resale_report/2023/thredUP_2023_Resale_Report_FINAL.pdf