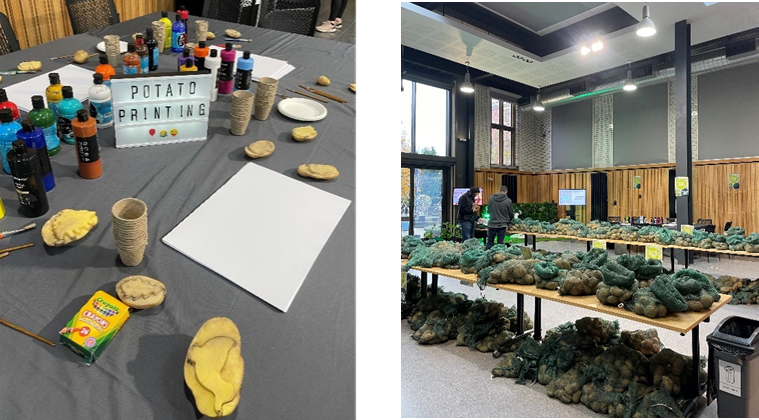
On Thursday 28th November the School of Natural and Environmental Sciences (SNES) hosted SpudFest, transforming the Boiler House into potato heaven. From research posters and company stalls to a potato-printing art station, the event brought together students, colleagues and local partners for a fun and informative day.

Why?
As part of their research, SNES has collaborated with NU Farms to drive innovation in plant and crop science. Every year, University farms Cockle Park Farm and Nafferton Farm grow tonnes of potatoes for research. When harvest season ends, rather than letting the produce go to waste, SNES shares the potatoes with the University community through SpudFest.
Over 1000 people attended the event this year, and over two tonnes of potatoes were given away!
Eat@Newcastle
One of the highlights of the day was the complimentary food samples, courtesy of Eat@Newcastle. The wedges and potato soup were fan favourites, drawing long queues of students and colleagues throughout the day.

Sustainability
Our team had a stand at the event to talk all things sustainability. Alongside us, Annita from Biffa highlighted the environmental impact of food waste with some eye-opening statistics:
- Food waste contributes to 8% of the UK’s total greenhouse gas emissions.
- UK households throw away 4.4 million fresh potatoes every day.
- Every day, 20 million slices of bread are thrown away. This is equivalent to a million loaves wasted daily!
Top Tips:
To keep your potatoes fresher for longer, store them somewhere cool, dry, dark – and away from onions. If they’re starting to look a little old, boil them for five minutes and freeze them. They’re perfect for roasting later! Also:
- Check out these stale bread recipes, to make the most out of your loaves.
- If you are a student in university owned accommodation, make sure to use your food waste bins
Men’s Pie Club
North east charity Men’s Pie Club joined the event to raise awareness of their mission to bring local men together over good food and friendly conversation.
‘It’s all about making pies, having a laugh, and getting to know a great bunch of lads in a relaxed, no-fuss environment.’ – Men’s Pie Club
Find out more about the club, here.

There was also a table to donate food items to the local foodbank! A great way to give back to the community.
SpudFest 2025 brought together research, sustainability, wellbeing and community spirit in one brilliant event. Huge thanks to SNES and Katy Sawyer for organising the event.
We are already looking forward to next year’s celebration of all thing’s potato!