A disposable vape is a pre-filled, electronic cigarette designed for one-time use. They have become a convenient alternative to cigarettes in recent years due to their affordability and availability. It is now predicted that over 360 million disposable vapes are thrown away in the UK every year, but only 17% of users recycle them in the correct recycling bins (Material Focus, 2023). This blog will explore the environmental dangers posed by these devices, while providing guidance on how to correctly dispose of them.

Image: Disposable vapes are often encased in colourful plastics, contributing to their detrimental impact on the environment (Source: Waste Managed, 2024).
Why are disposable vapes an environmental problem?
From the 1st of June 2025, the sale of disposable vapes will be banned in the UK to protect children’s health as they have become increasingly popular among young people. But why are these devices so bad for the environment? Let’s explore the key reasons…
- They’re made of plastic
Disposable vapes contribute significantly to the growing problem of plastic waste. Vapes left on the street are likely to break down into microplastics that flow into drains and pollute water systems (Truth Initiative, 2021). They’re also very difficult to recycle as they are made of many different parts including batteries and circuit boards, as well as plastic – components that must be separated. Moreover, plastic takes hundreds of years to breakdown, meaning that your vape will most likely outlive you!
- They contain harmful chemicals
Vapes are made of plastic casing, lithium batteries, copper wire and other components. Separating these materials during the recycling process is both labour-intensive and expensive. Additionally, the toxic compounds in vapes, are also prone to leach into soil and water systems, contaminating animal habitats.
Both lithium and copper are finite resources. They are necessary for infrastructure, electric vehicle batteries and charging stations (Sky News, 2024). Using these elements in vape production wastes valuable materials that are essential for advancing green technologies.
- They can cause battery-related fires
When vapes are crushed, their lithium can overheat and ignite fires. The London Fire Brigade has responded to more than 200 fires caused by lithium batteries in the last two years (BBC News, 2024). If disposable vapes are disposed of in the general waste bin, they are more prone to being crushed and compressed, and therefore more likely to cause fires on waste vehicles and in waste facilities, potentially endangering waste workers and causing unnecessary damage.
How to dispose of vapes responsibly?
Up to 80% of a disposable vape can be recycled, and there are two main ways you can dispose of your vapes responsibly: organising a collection, or taking your vape to an electronics recycling station.
See below for some key recycling points in Newcastle. As shown, most Tesco Express stores have electronic recycling points. Many points are also near the University campus, making it extra convenient for disposal!
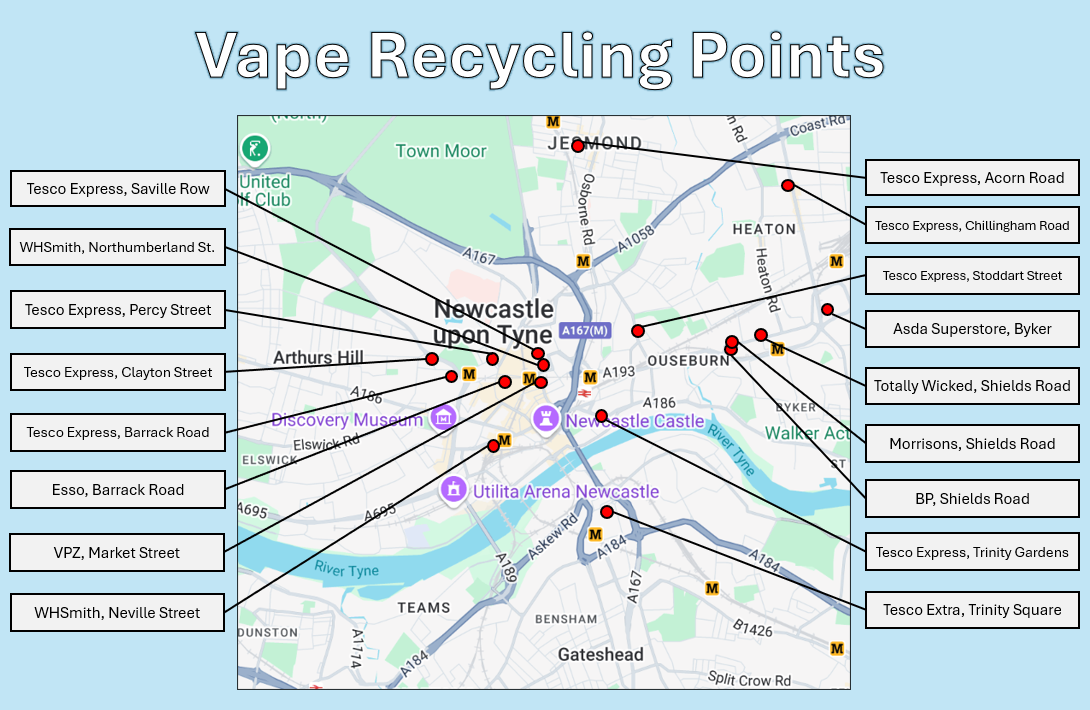
Image: Some key locations around Newcastle that contain bins for electronic devices, e.g. vapes.
A second option for disposal is arranging a Waste Electrical & Electronic Equipment (WEEE) collection to your house. These are free for all Newcastle City Council residents who have their own front door access on the ground floor. Simply book a day online, and leave your vape(s) on your doorstep inside a plastic bag the night before. Your items will be collected and disposed of safely.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, while purchasing a disposable vape may seem convenient, its disposal is far from simple. As their banning date becomes imminent, it is essential to ensure that any remaining devices are disposed of responsibly. An item that may only last you a week, could be harming the planet for decades!
For more information on recycling items on campus, check out our Waste A-Z. If you would like to search for your nearest electronic recycling point, use the handy Recycle Your Electricals search engine. To book a WEEE collection, visit the Newcastle City Council booking page.
Reference List:
BBC News. (2024). The environmental impact of disposable vapes. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/articles/cy943vpr7vgo
Material Focus. (2023.). Disposable single-use vapes thrown away have quadrupled to 5 million per week. https://www.materialfocus.org.uk/press-releases/disposable-single-use-vapes-thrown-away-have-quadrupled-to-5-million-per-week/#:~:text=Material%20Focus%20has%20found%20that%20UK%20adults%20report,could%20instead%20be%20powering%20nearly%205%2C000%20electric%20vehicles
Sky News. (2023). Why are disposable vapes bad for the environment? https://news.sky.com/story/why-are-disposable-vapes-bad-for-the-environment-13059299
Truth Initiative. (2021). The toxic plastic problem: E-cigarette waste and the environment. https://truthinitiative.org/research-resources/harmful-effects-tobacco/toxic-plastic-problem-e-cigarette-waste-and-environment
Waste Managed. (2024). How to dispose of vapes: Are they recyclable? https://www.wastemanaged.co.uk/our-news/recycling/how-to-dispose-of-vapes-are-they-recyclable/