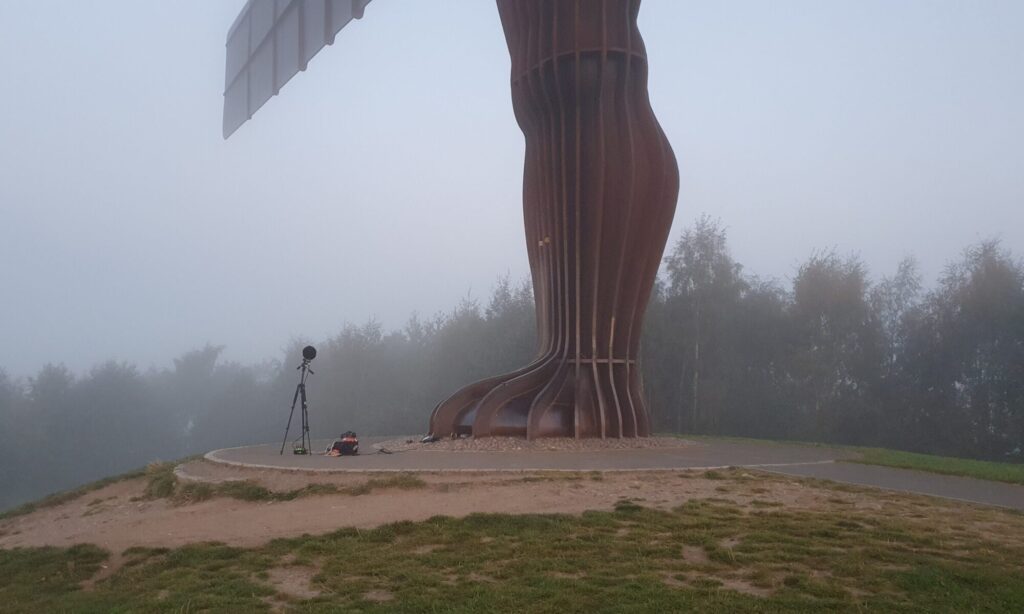
I wrote in a recent post about presenting a paper on the ‘Sounding the Angel’ project at the Spontaneous Memorials conference at Manchester University, which was organised by Kostas Arvanitis. Here, I reflected on the importance of sound in relation to spontaneous memorialisation, which was evident both in the other papers for the panel and in the piano recital that followed.
In this post, my focus is on a panel that I was invited to chair, which included a presentation from a team at the National Archives. Hannah Jones, Mike Rogers, and David Morris from the National Archives UK gave a paper entitled ‘Rapid Response Collecting: developing practical guidance for the archives sector’. They explained that the National Archives hold an advisory and leadership function for archives in England, offering a wide range of support and guidance through their Archives Sector Leadership department. The department is responsive to needs in the sector, and it became apparent that there was an emerging gap of knowledge in relation to collecting, documenting and archiving spontaneous memorials. In 2024, the department therefore commissioned a piece of guidance on best practice in this area, drawing on the advice of archivists and curators who had already been involved in archiving spontaneous memorials. The conference paper spoke about the approach that was taken in commissioning the guidance, and provided practical examples and suggestions.
One of the leading principles adopted in developing the guidance was not to be proscriptive but rather to present a range of different approaches. Drawn from examples around the world, the guidance aimed to offer potential approaches in often sensitive and emotive situations, with high levels of media interest. The guidance covered first response, and short and medium-term actions and strategies. Seeking to be flexible and inclusive in their definition of spontaneous memorials, the team did not restrict their examples to attacks and disasters, but also featured case studies from other scenarios, including the 2001 Foot and Mouth outbreak, the Covid-19 pandemic, and documenting student protests.
Speaking with the National Archives team after the panel, I was delighted to hear that they were interested in including the ‘Sounding the Angel’ project as an additional case study to accompany the guidance. The team explained that the project was very different from other examples they had encountered. On the one hand, this was related to the nature of the memorial itself, which commemorates many separate, unconnected people and events, and has arisen in relation to a work of public art. On the other hand, our documenting of the memorial through sound, rather than by the collection and storage of objects, also offered a novel approach to archival practice. Using a template of questions and prompts from the National Archives team, I developed the learning from the project into a case study, and it was fascinating to think about the work from the point of view of what other teams might find most useful in practice.
The case study is now on the National Archives website and you can read it here. Many thanks to Mike, Hannah, and David for their generous invitation to include the project as part of such a valuable and carefully considered resource.