Each year, Newcastle University undergoes an external audit to ensure that our Environmental Management System (EMS) and Energy Management System (EnMS) meet the requirements of the ISO 14001 and ISO 50001 standards. These audits are rooted in our list of compliance obligations (COs). In this blog, we will explore what compliance obligations are, some examples, and how they affect the wider University community.
What are compliance obligations?
Compliance obligations are described by ISO as:
“Legal requirements that an organization has to comply with and any other requirements that an organization has to or chooses to comply with”
The University has a register of environmental and energy commitments it must adhere to, like those required by the law and others which are voluntary. We work with Barbour EHS, a consultancy that provides compliance and information services, to help us keep our obligations register up-to-date, especially when new legislation comes into place.
During the external audit, auditors review the list of compliance obligations and assess how these requirements are being met. Failure to comply with these obligations could result in the University losing its ISO accreditation.
What are some examples of compliance obligations?
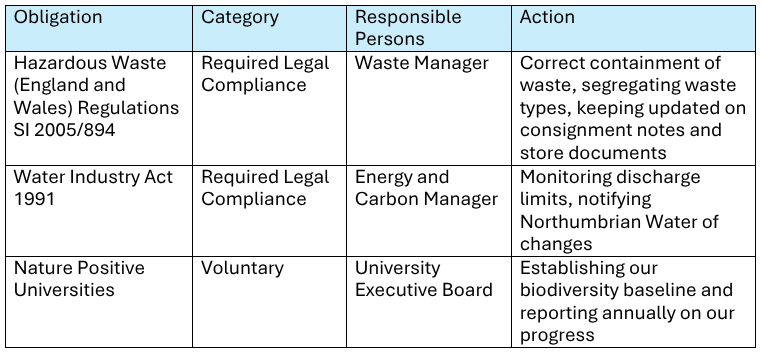
The concept may sound rather abstract, so here are some examples of obligations on our register.
As you can see, many of the obligations link back to our key themes, looking at carbon, water, waste and biodiversity. This highlights how compliance obligations serve not just as checkboxes, but as practical drivers of environmental action across departments.
Nature Positive Universities is just one of many voluntary obligations we’ve committed to, alongside our Net Zero targets, membership to the EAUC, participation in the People & Planet University League, the Race to Zero campaign, the SDG Accord, and the Concordat for the Environmental Sustainability of Research and Innovation Practice.
How do we integrate compliance obligations into our work?
Compliance obligations guide how we plan, implement, and monitor environmental and energy practices across campus. The process usually begins with changes in legislation or voluntary initiatives, which are then translated into internal actions. These updates are reviewed during both internal and external audits, helping us track progress and identify areas for improvement.
For example, when the Simpler Recycling legislation came into play in March 2025, we responded by reviewing how waste was being managed in all areas of campus, especially student accommodation. This led to collaboration with our waste contractor, Biffa, to introduce food waste bins and expand glass recycling across key locations. These operational changes directly support compliance obligations related to waste segregation and management. Auditors can assess these during their visits and may even offer feedback in the form of an OFI (Opportunity for Improvement), which helps us refine our systems further.
How are students and colleagues involved?
From the table above, you can see that COs extend the scope of the Sustainability Team’s work – we work closely with colleagues across the University to meet them. Everybody at the University plays a role in meeting environmental responsibilities. From Estates designing efficient building systems and maintaining green spaces, to individuals recycling correctly and using energy efficiently in their workspaces, everyone plays a key role in our EMS and EnMS.
COs are all over, even when you may not notice. For instance, most University buildings have an environmental noticeboard near their entrances, displaying Display Energy Certificates, required under the Energy Performance of Buildings Regulations.
Students are also a key part of this process. Under the Waste Duty of Care Code of Practice, waste producers (including students in accommodations) are responsible for sorting their waste correctly. Additionally, by completing travel surveys, both students and colleagues are contributing to voluntary efforts aligned with the Road Traffic Reduction Act 1997 and the Transport Act 2000.
From waste and water to biodiversity and transport, compliance obligations influence many day-to-day decisions at the University. They help ensure we’re not only meeting legislation but actively working toward a more sustainable campus.
If you’d like to find out more about our environmental and energy management systems, read our blog, or check out our webpage. For any sustainability queries, please email us at sustainable-campus@newcastle.ac.uk