Dr Paul Quinn speaks to BBC Radio 4 about Newcastle University’s efforts to improve our resilience to the extreme weather events of 2012
Senior Lecturer in Catchment Hydrology and CESER researcher, Dr Paul Quinn was invited to take part in a special programme for BBC Radio 4’s Farming Today on extreme weather conditions in 2012. The programme aired on Jan 2nd, and is currently available via the BBC iPlayer.
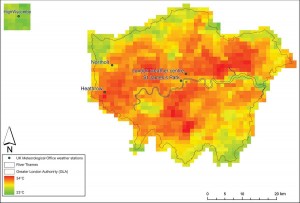
Paul was involved, alongside Farming Consultant Lindsay Hargreaves and a number of farmers from across the country, to discuss their experiences and understanding of drought and floods last year, and consider what 2013 might bring. The unusually dry winter (in England and Wales) preceding Spring 2012 led to a severe drought in the first months of the year and the resulting hosepipe ban in March. Across the border in Scotland, however, was a very different situation, with 2011 being the wettest on record for 100 years and no signs of let up into 2012, where some parts actually received less than average rainfall for the latter part of the year!
In England, the hosepipe ban became a somewhat ironic prelude to what turned out to be the wettest summer since records began, and the accompanying cold temperatures alongside the sheer amount and longevity of rainfall completely devastated crops nationwide including cereals, potatoes and fruit. Individual farmers speaking on the BBC programme reported losses of between 15% (potatoes) to 90% (apples) on the previous year, not to mention the knock-on effects of such a late, low quality harvest; namely barns full of grain blocking cattle coming in for winter and further wet/icy conditions making removal of that grain impossible.
The solution for farmers to such extreme weather (which we know under conditions of climate change will most likely increase), is better soil management, according to Paul. He explains that our soil is generally in a poor state, so does not store as much water as it used to. This is due to overuse and the fact that modern farming practices often don’t allow the soil to function properly. Paul, alongside other members of CESER and the NIReS Terrestrial Theme at Newcastle University, believe that it is possible to create a climate resilient landscape that results in positive relationships between food production, soil and water management, biodiversity and habitat protection, pollution reduction and even carbon storage. This requires collaboration between specialists in different fields (pardon the pun!), something which is being made possible through CESER and the NIReS Terrestrial Theme, and will result in more opportunities for research into catchments and landscapes with multiple functions that are more resilient to the changes in climate that we are witnessing in the UK but also globally, as described on the programme.