#EmbraceEquality
Newcastle University colleagues share their thoughts on #embraceequity International Women’s Day 2023
As we celebrate International Women’s Day, it is important to reflect on the progress made towards gender equality and recognise the work that still needs to be done. The theme for International Women’s Day this year is #embraceequity.
The difference between equality and equity is subtle yet important. Equality means each individual or group of people is given the same resources or opportunities. Equity recognises that each person has different circumstances and allocates the exact resources or opportunities needed to reach an equal outcome. Equity is vital as it recognises that everybody starts from different places in life, and if we embrace equity, it promotes inclusion and diversity in everything we do.
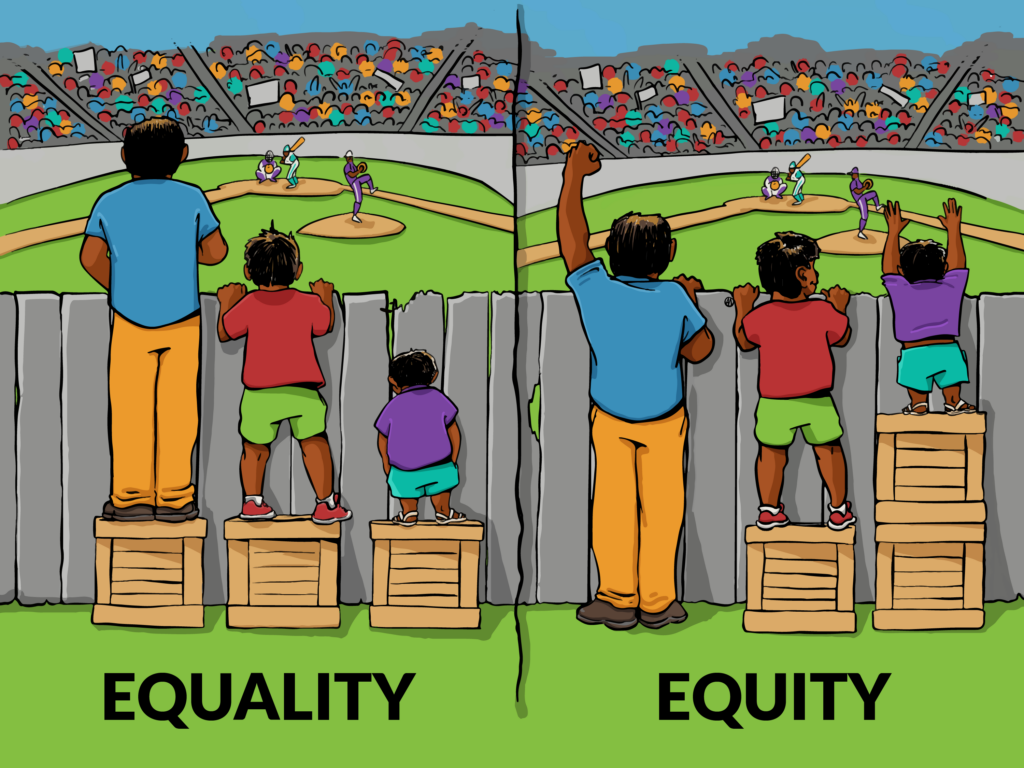
For International Women’s Day, we asked our colleagues three questions.
- What does equality mean to you?
- What does equity mean to you?
- Can you share an example of when something you have undertaken yourself has led to a positive change in terms of gender equity? This could be in your personal or professional life.
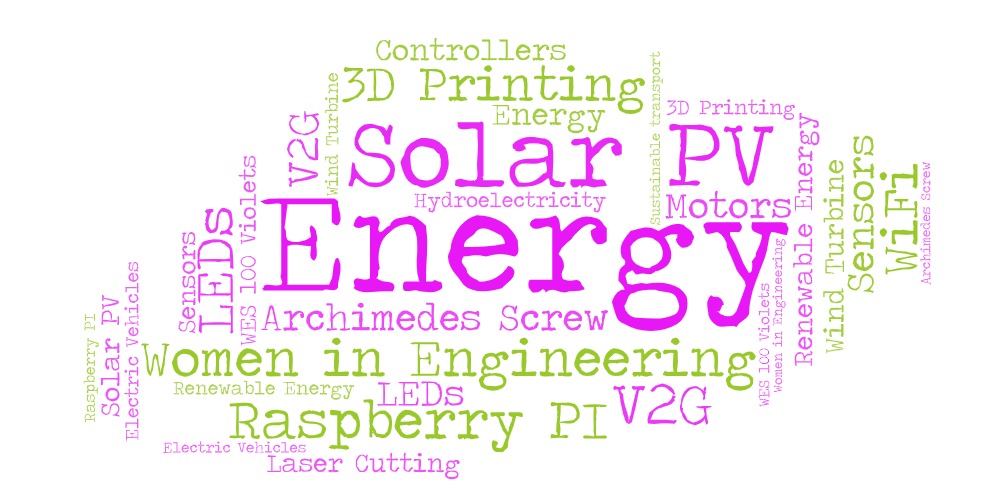
We used the responses from the first two questions to create a word cloud, pictured in Figure 1.

“I encouraged a female PhD student to apply for a doctoral prize fellowship which she would not otherwise have considered. She successfully won the fellowship, and it has kickstarted her post-doctoral research career.”
“I had an intern helping me who was a single parent doing her bachelor’s degree and I was happy for her work hours to be flexible around her and made the effort to find her extra funding to continue the work further.”
“I was a mentor to a teenage girl through the Girls Network and hope that I supported my mentee even in small ways to realise her potential as a young woman.”
“A recent funding application was undertaken anonymously and lead to a 50/50 gender split, even age split with more ECRs and more ethnic diversity. All of these attributes help to create a more diverse and positive research culture.”
“In an event me and a few friends were running, we decided to dedicate performance slots to female artists after having male dominated line-ups for a long time. We received a positive response from our female attendees, discovered some great artists and the opportunities have helped several of the artists progress their music careers.”
One of the biggest barriers to equity is the cost of childcare, which disproportionately effects women with children as they are typically the primary care givers. We acknowledge all responses received in our survey and are aware of challenges and barriers that are present. Our colleagues and the processes that are implemented are continuously being improved to ensure that all voices are heard. It is important to challenge behaviour that unfairly discriminates against anyone in the workplace. We hope that our anonymous survey will encourage others to share their stories in the future, as well as embracing the benefits and barriers of embracing equity that exist.
See here for more inspirational stories.
#IWD2023 #EmbraceEquity