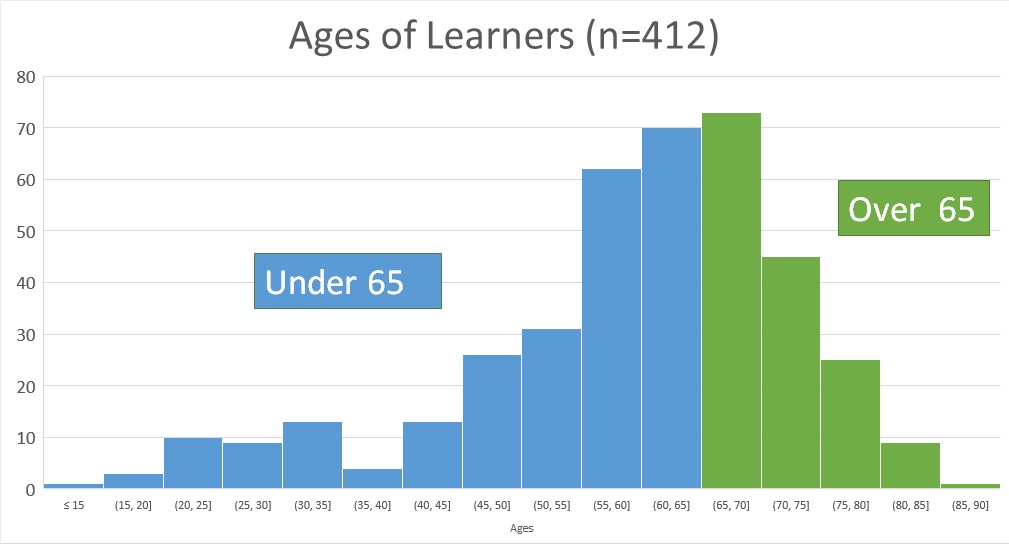
Ageing Well: Falls is a four week (2 hours a week) free online course, which starts on 5 September 2016. Previous learners really valued this engaging course which is having a real effect on people’s lives.
This course was excellent, it gave a lot of good information and dispelled many myths about “only old folks have falls”, as well as giving resources to check when problems arise.

As we make the finishing touches to the course before it starts, we asked Dr James Frith, Lead Educator, a few questions which come up regularly:
Are falls really that dangerous?
James: Yes. Falls are hugely common and as we get older our bodies are less robust and are more likely to be injured during a fall. Serious injuries include broken bones and head injuries or serious bleeding. A broken hip can be devastating for some people. But for some people the loss of confidence following a fall can be just as disabling as a physical injury. Fortunately we can reduce the risk of falling and the associated injuries.
What is the most common story you hear from your patients?
James: Falls are complex and are rarely caused by a single factor. in each person who falls there are a mix of factors which contribute, so there is not really a typical type of fall. However, common things which I come across are:
- Falling on the bus as people get up from their seats before it has stopped.
- Putting out the bins in wet or windy weather.
- Getting up too quickly to answer the telephone or the door.
- Slipping in the bath or shower.
What can increase a person’s risk of falls?
James: Researchers have identified hundreds of risk factors for falls, so we tend to stick to the ones that we can do something about. The main risks are having a poor gait or balance, poor eye sight, dizziness, some medications, and hazards in the home or on the street, but there are many more.
What can a person do to reduce the risk of falls?
James: Sometimes it can come down to common sense, such as keeping stairs free from clutter, turning on the lights and reporting dizziness to the doctor. But there are other simple ways too, such as keeping the legs active and strong through gentle exercise, having a medication review with a doctor or pharmacist, avoiding dehydration and having walking sticks measured by a professional.
What is the best way to recover from a fall?
James: If someone is prone to falls they should consider wearing a call alarm or keeping a mobile phone in their pocket, just in case they need to call for help. Some people can learn techniques to help them stand following a fall – usually from a physiotherapist or occupational therapist. In the longer term anyone who has fallen or is at risk of falls should seek help from a health professional to try to prevent future falls. Sometimes falls can be due to medical conditions which can easily be treated.
Everyone knows someone who has fallen. Why not join our friendly team of falls specialists and thousands of people like you to find out what you can do to help yourself, your family, friends or people you care for?
The lead educators were warm and engaging, and they were generous with their knowledge and expertise.
I liked the interaction between participants. It makes you feel you are not alone in your experiences.
Sign up now at www.futurelearn.com/courses/falls





 You can watch Angela receive her award (45 minutes and 8 seconds) and see her speech (45 minutes 50 seconds) in the congregation video at:
You can watch Angela receive her award (45 minutes and 8 seconds) and see her speech (45 minutes 50 seconds) in the congregation video at: 

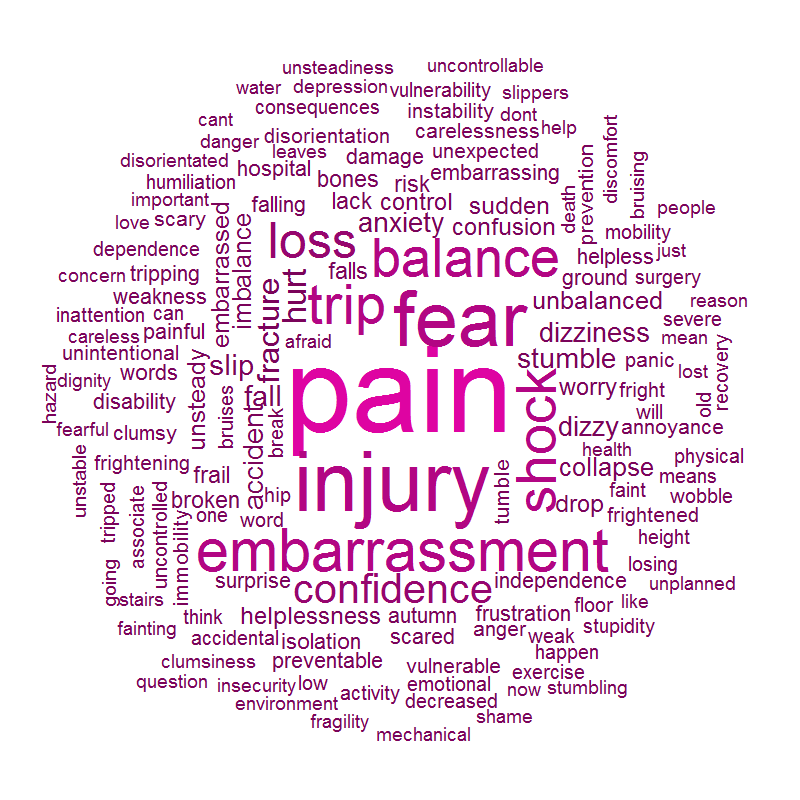 For a moment, it seems as though all the eyes in the world are focussed on us, just as we are feeling particularly vulnerable, lying on the ground. Given that almost everyone who has ever walked on the earth will have experienced a fall at some point in their life, why is it so embarrassing to fall in public? In fact, we can all probably empathise with someone in this position, having been through it ourselves.
For a moment, it seems as though all the eyes in the world are focussed on us, just as we are feeling particularly vulnerable, lying on the ground. Given that almost everyone who has ever walked on the earth will have experienced a fall at some point in their life, why is it so embarrassing to fall in public? In fact, we can all probably empathise with someone in this position, having been through it ourselves.



