We are delighted to announce some new journal titles and other resources available from the University Library.
Ones useful for ECLS staff and students are :
New journals
Children Youth and Environments
This title covers the latest news on children, youth and their environments. It is dedicated to improving the lives of young people and is aimed at students, researchers, policy makers and professionals. Access is from volume 13 onwards.
Topics in stroke rehabilitation
Published 8 times per year, this journal focuses on the study and dissemination of theoretical and practical information related to the subject of stroke rehabilitation. Reviews and reports common clinical practices, state-of-the-art concepts, and new developments in stroke patient care and research. Access from volume 3 onwards.
Seminars in speech and language
Published 5 times per year, this journal provides information on clinical advances in speech and language pathology, offering diagnostic procedures, screening and assessment techniques, treatment protocols, and short- and long-term management practices. Backfile access for years 1984-1999.
Language Learning
A quarterly journal which publishes research articles that systematically apply methods of inquiry theories from linguistics, psycho-linguistics, cognitive science, ethnography, socio-linguistics, sociology, semiotics, educational inquiry and cultural and historical studies to address fundamental issues in language learning. Access is from volume one.
New Resources
We’ve bought five new eBook collections from Bloomsbury, comprising over 150 titles across a wide range of subjects. The new collections are: Education 2018; Film and Media 2017; Linguistics 2018; Literary Studies 2018.
All the new titles are individually catalogued on Library Search, or you can access a full listing of collection contents on this page.
We have access to De Gruyter’s enire ebook collection until June 2019, after which we will buy access to the most well used titles. This currently covers over 27,000 titles related to numerous subjects including education and social science. All titles are catalogued individually on Library Search.
Emerald eBook collection
We have bought a range of eBooks from Emerald these are all cataloged and available on Library Search.
Titles include:
The future of learning and teaching in next generation learning spaces
Accelerating changes in schools; leading rapid successful and complex change initiatives
Teaching excellence in higher education
Sunday Times Digital Archive
We’ve now added the archive for 2007-2017 to our newspapers collection.







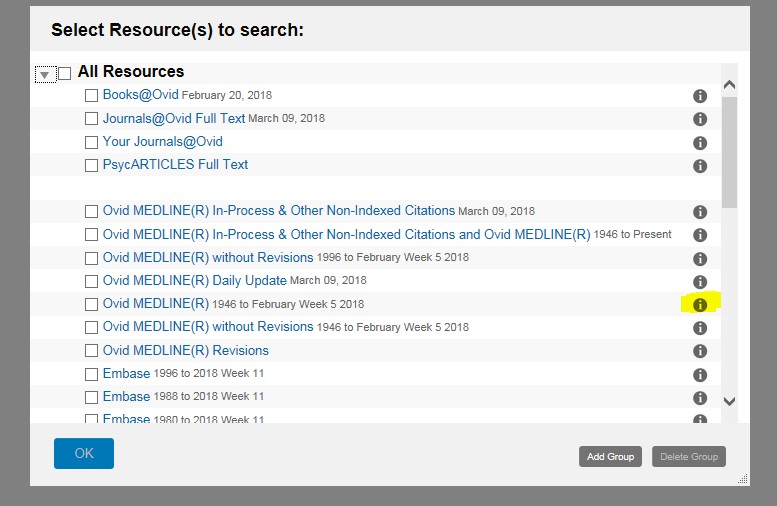 Once you have decided on which database to search within OVID, then all you need to do is to tick the box next to the database you would like to search and then select ‘OK’.
Once you have decided on which database to search within OVID, then all you need to do is to tick the box next to the database you would like to search and then select ‘OK’.