 Laura-Jayne Beattie, a final year Law School student, takes a look at Box of Broadcasts, and reviews a film she watched using it (a Law Library favourite!).
Laura-Jayne Beattie, a final year Law School student, takes a look at Box of Broadcasts, and reviews a film she watched using it (a Law Library favourite!).
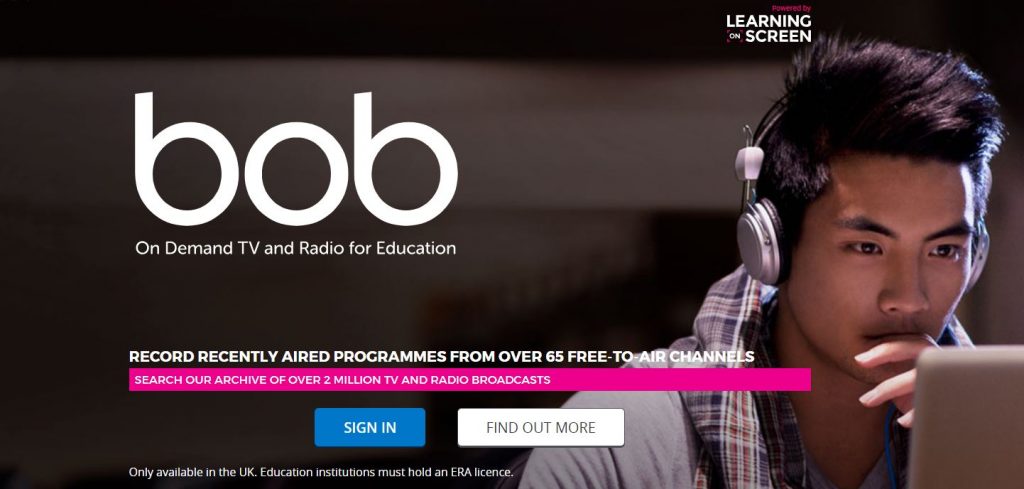
BoB (Box of Broadcasts), available to all Newcastle University students regardless of degree discipline, is an excellent resource. Best of all, it’s FREE for students studying at Newcastle (just what a student wants to hear)! You just have to select the university from the list of institutions, sign in with your university login details (username and password), and away you go! You’re free to explore the thousands of television programmes, radio broadcasts and films available on the website. It’s incredibly easy-to-use, and reminds me a lot of Netflix, but is less guilt-free as most of these programs and films are education-related in some way. The broadcasts may relate to your degree or another academic interest of yours (e.g. psychology-related films).
You can watch live TV, or search (by name) for a pre-recorded film, radio show or television programme. The system holds over 2 million broadcasts, which have been shown on television or aired on the radio at some point since the 1990s. If you don’t have a specific film or programme in mind which you would like to watch, why not try out the advanced search feature? Click on the ‘Search’ icon, then on ‘Search options’, change as many or as little options as you like, and then hit ‘search’! A list of broadcasts matching your search criteria will be shown. I’m sure there will be at least one that interests you!
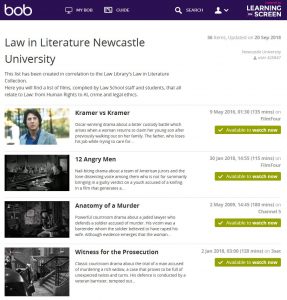 After a few minutes of exploring the website, I decided to choose a film from the ‘Law in Literature Newcastle University’ playlist. To find this, I clicked on the ‘Search’ icon (on the tab across the top) and selected ‘Public Playlists’. I then typed the playlist’s name into the search box. I was surprised at how many titles were available within this collection (all related to Law). I chose to watch ‘Legally Blonde’, a personal favourite of mine but one that I haven’t watched for years.
After a few minutes of exploring the website, I decided to choose a film from the ‘Law in Literature Newcastle University’ playlist. To find this, I clicked on the ‘Search’ icon (on the tab across the top) and selected ‘Public Playlists’. I then typed the playlist’s name into the search box. I was surprised at how many titles were available within this collection (all related to Law). I chose to watch ‘Legally Blonde’, a personal favourite of mine but one that I haven’t watched for years.
Here’s what I thought…
‘Legally Blonde’, a fun-filled film showcasing a story of love and success, shows Law in a new perspective and is a must-watch for any Law students (Yes, even you boys). It’s a feel-good film, and is motivational in terms of showing that anyone really can succeed if they put their mind to it! It’s particularly perfect for any law student who feels ‘out-of-place’ with the supposed societal ‘ideal’ of who should be studying law.
Defying all pre-conceptions derived from her appearance, Elle Woods gains a place at the prestigious Harvard Law school. While this was initially to follow her ex-boyfriend, who broke her heart just before he proceeded to study Law there, she soon develops a passion for Law and becomes top of the class. She helps to win a case while on work experience using her knowledge of fashion, and later delivers an inspirational speech at graduation saying words like “you must always have faith in yourself”. When making this speech, it’s clear from the smiles in the room that she has won the hearts of students and staff alike and made lifelong friends with her heart-warming personality. Graduating with a job in a high-ranking law firm, she puts her career ahead of everything and even rejects her ex-boyfriend who wanted her back towards the end of the film.
‘Legally Blonde’ relates to Law, as Elle overcomes sexual harassment while on work experience (Employment Law). Initially, Elle doesn’t report the man and decides to drop out of law school- possibly as she thought she wouldn’t be believed or that what happened wasn’t actually a crime (a common occurrence amongst victims in reality). Parts of Law lectures are filmed, and Elle overcomes stereotypes that are derived from her appearance (blonde female who evidently loves the colour pink) (Law, Gender and Sexuality). Despite not being a typical Harvard student, she still succeeds without letting these stereotypes stop her.


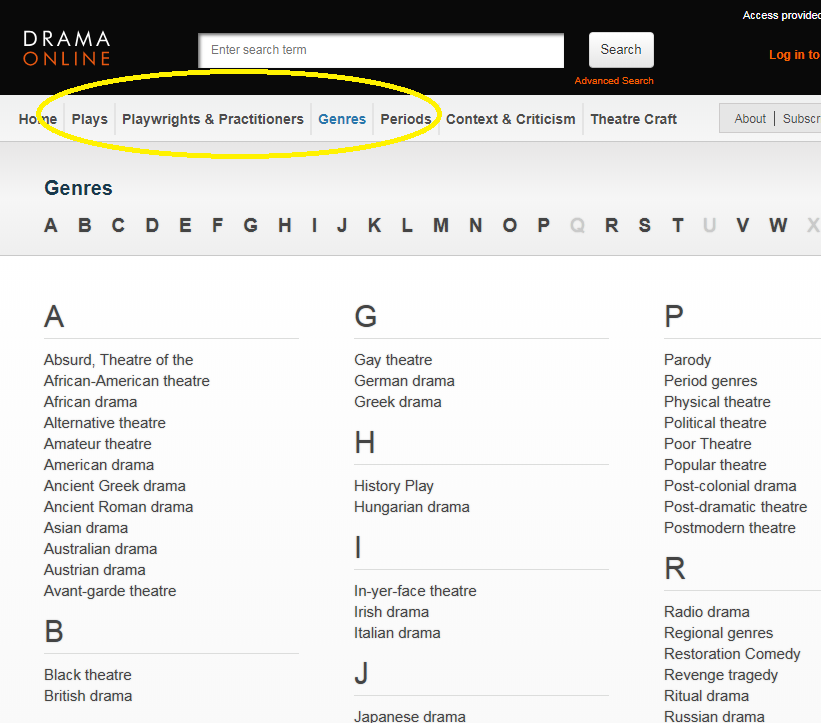 or you can search/browse them all in various ways on the Drama Online site.
or you can search/browse them all in various ways on the Drama Online site.
 Laura-Jayne Beattie, a final year Law School student, takes a look at Box of Broadcasts, and reviews a film she watched using it (a Law Library favourite!).
Laura-Jayne Beattie, a final year Law School student, takes a look at Box of Broadcasts, and reviews a film she watched using it (a Law Library favourite!). After a few minutes of exploring the website, I decided to choose a film from the ‘Law in Literature Newcastle University’ playlist. To find this, I clicked on the ‘Search’ icon (on the tab across the top) and selected ‘Public Playlists’. I then typed the playlist’s name into the search box. I was surprised at how many titles were available within this collection (all related to Law). I chose to watch ‘Legally Blonde’, a personal favourite of mine but one that I haven’t watched for years.
After a few minutes of exploring the website, I decided to choose a film from the ‘Law in Literature Newcastle University’ playlist. To find this, I clicked on the ‘Search’ icon (on the tab across the top) and selected ‘Public Playlists’. I then typed the playlist’s name into the search box. I was surprised at how many titles were available within this collection (all related to Law). I chose to watch ‘Legally Blonde’, a personal favourite of mine but one that I haven’t watched for years. Are you preparing a dissertation or project, or will be doing so soon?
Are you preparing a dissertation or project, or will be doing so soon?