Do you need help to understand your mental health and wellbeing?
Are looking to understand your subject from a different point of view?
Then take a look at the collections below. These will get you reading around and outside of your subject and could benefit your health and wellbeing. Both collections can be found in the Quiet Study area of the Walton Library.
Be Well@NCL

Be well@NCL is a collection of books designed to help manage and understand common mental health conditions and wellbeing. Reading a book by someone who understands what you are facing can help you start to feel better. The books within the collection are recommended by professionals and are available to borrow. The Philip Robinson and Walton libraries have the same collection of books.
Content of the collection
The collection offers books that can help with a wide range of issues and concerns. The collection includes titles that offer more healthy ways of thinking, such as practicing mindfulness and challenging unhelpful thought patterns. There are also books about common feelings, experiences, and issues, such as:
- Anger
- Anxiety – including health anxiety and social anxiety
- Bereavement, loss and grief
- Body image issues and Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- Caring for someone with a mental health issue
- Depression – including postnatal depression
- Eating disorders and eating distress
- Low self-esteem
- Mood swings
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Phobias and panic
- Sleep problems
- Stress
If you find the book you are reading is not helping, please contact your GP or health professional. If you are a student you can also contact the University’s counselling team.
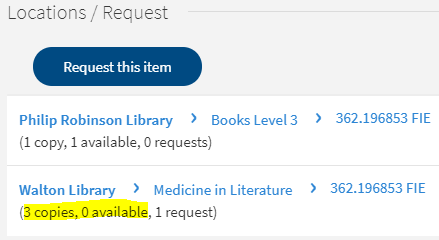
If the book you want is out on loan then please make a Reservation. If there is high demand for a book this alerts library staff to potentially order more.
Pick up a Be well@NCL postcard from the Walton Library desk or find out more here.

The Medicine in Literature collection captures the complexities of what it means to be human through a wide range of literary genres. Representations of illness, dis-ease, healing and health are interwoven themes that give voice to a diversity of perspectives and experiences. If you are interested in exploring your subject from a different viewpoint or simply want to broaden your reading, dive right in! The collection includes books and DVDs.
Topics covered include:
- Alzheimer’s
- Anxiety
- Autism
- Bipolar Disorder
- Brain Disorders
- Cancer
- Coma
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Dementia
- Depression
- Eating Disorders
- Epilepsy
- HIV/AIDS
- Leukaemia
- Locked-In Syndrome
- Mental Illness
- Motor Neurone Disease
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- Parkinson’s
- Polio
- Schizophrenia
- Stroke
Go and have a look at both of these collections in the Quiet Study area of the Walton Library.