We have access to the Times Literary Supplement (TLS) archive from 1902-2014.
The archive brings you the full content of this world-renowned weekly literary and arts publication, dating back to its first issue. For over a century, the TLS has published reviews, features, debates and original works from across the arts world, not to mention its legendary letters page!
Many of the world’s most notable writers and thinkers have contributed to the TLS over the decades, including T.S. Eliot, W.H. Auden, Seamus Heaney, Noam Chomsky, Virginia Woolf, Bertolt Brecht and Umberto Eco. Until 1974, contributions published in the TLS were often anonymous, but the digital archive now reveals the identity of all contributors.
To find out more about the TLS, click Research Tools to read a selection of essays about different periods of its history.

You can browse the TLS by date to find a specific issue, or search in various ways (choose Advanced Search to see all options, including searching by contributor, book title, or document type.)
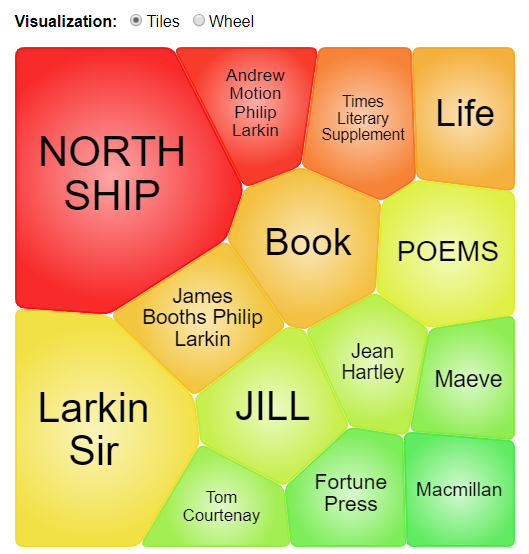
Additional search features on the home page include Term Frequency, to trace how often a word, phrase or person has featured in the TLS over the years, and Topic Finder, to explore and visualise connections between topics.
As the TLS archive is published by the company Gale, you can cross-search it with any of the other Gale archives to which we have access, via Gale Primary Sources.