I recently needed to connect my phone to a wireless network and the only connectivity available was a wired VPN on my notebook. It turns out that in Windows 7 and Windows 8 it is possible to turn a wireless enabled machine into a hotspot that any device can use!
Instructions
1) Run an elevated command prompt (Right Click > Run as administrator) and run the command:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=<networkname> key=<password>
Where <networkname> is your choice of name for your Hotspot and <password>is a strong secure password.
For example
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid="James WiFi" key="G0dBl3ssTheIntern3t"
2) This will create a connection called ‘Wireless Network Connection 2’ which is a Microsoft Virtual WiFi miniport adapter. Rename the connection as ‘Wifi Hotspot’
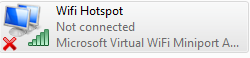
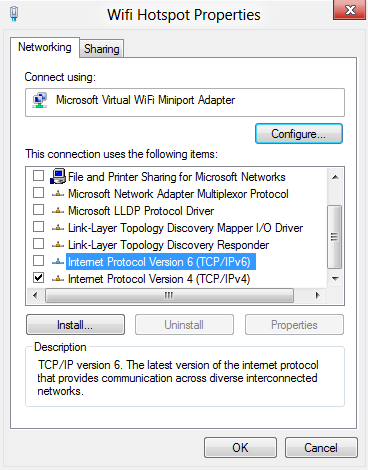
3) Browse to the properties of the adapter and uncheck all of the options apart from Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
4) Browse to the properties of the Internet connected adapter or VPN connection and select the sharing tab. Tick the first box as below and select Wifi Hotspot as the Home n.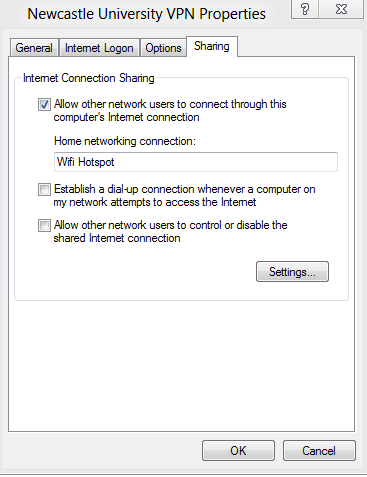
5) Create a shortcut on the Desktop called ‘Start WiFi Hotspot. This will let you switch on the hotspot on without having to type the commands. In the location box type:
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
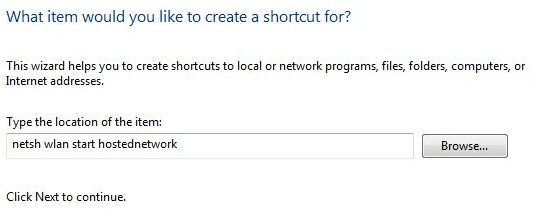
6) Create another shortcut on the Desktop called ‘Stop WiFi Hotspot. This will let you switch off the hotspot on without having to type the commands. In the location box type:
netsh wlan stop hostednetwork
7) Note: The shortcuts must be run as an Administrator (Right Click > Run as administrator)
8) And that’s it! You should now be able to connect to your hotspot and use the internet wit other wireless enabled devices such as your Phone, Console or other laptops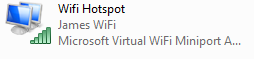
To remove the settings run the command below and do change the WiFi Hotspot name or password just run the first command again with the new details.
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=disallow ssid=<networkname> key=<password>










