This year for Space Day, Earth Science student, Jade, explains all about the structure of the sun, moon and the planets in the solar system.
The Sun
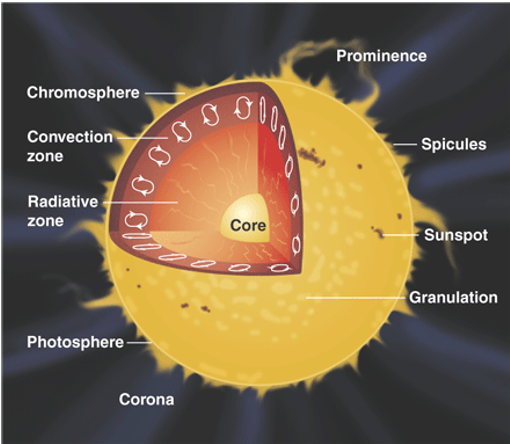
- The sun isn’t a planet, it’s a star in the Yellow Dwarf stage of its life.
- The sun is in the middle of the solar system and is a ball of hot gases (mostly helium).
- Even though it is made of gases it still has 6 layers within it:
- Core – Where solar energy is generated which is where the heat comes from.
- Radioactive zone
- Convection zone – Where the heat travels up to the surface.
- Photosphere – Visible surface
- Chromosphere – Thin layer of gas
- Corona – Thick atmosphere extending for millions of miles and it’s only visible during a solar eclipse
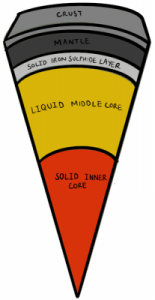
Mercury
- Mercury is the smallest planet in the solar system.
- It experiences extreme temperatures, both hot and cold. The heat is from being so close to the sun and the cold is due to the lack of atmosphere which causes the heat to escape.
- Mercury’s interior is made up of a solid inner core, liquid middle core and a solid layer of iron sulphides. Then there is a mantle and a crust which together are around 400km thick at and mostly made from silicate minerals.
- On the surface it has craters from meteorite impacts and lava plains from past volcanism that ended around 750 million years ago.
- Although it has extreme heat there is ice at the poles, even during the heat as the ice is in the shadows of craters.
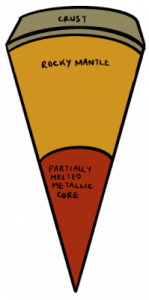
Venus
- Second closet planet to the sun.
- It has an iron core, a rocky mantle and a thin crust, similar to Earth.
- As the rocky mantle moves underneath the crust it bulges and forms mountains and volcanoes.
- There isn’t any water on Venus due to its high temperature.
- It has an atmosphere mostly made up of Carbon Dioxide, but it doesn’t have any wind due to its slow rotation.
- It can sometimes rain sulfuric acid.
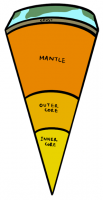
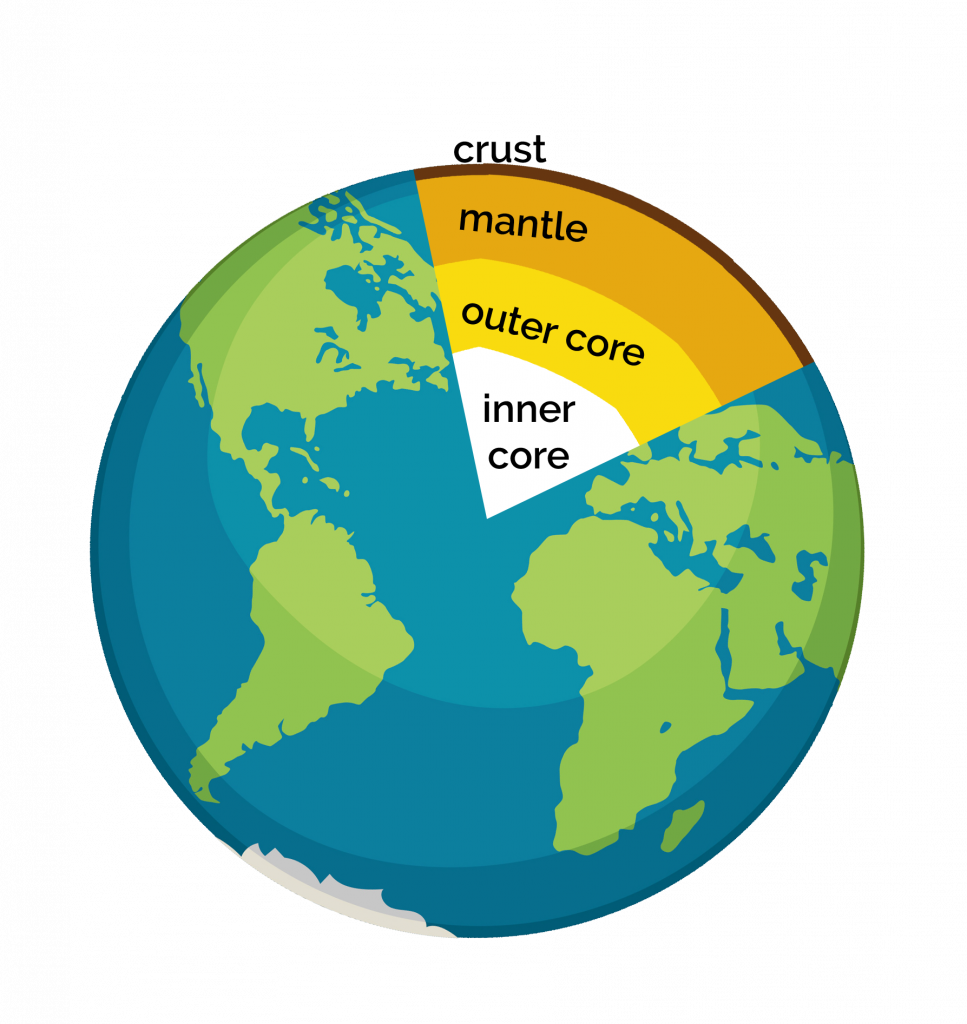
Earth
- Solid inner core made of iron and nickel.
- Liquid outer core also made out of iron and nickel.
- Rocky mantle which is mostly a fluid which convects heat from the core to the surface. As it convects, it forces the plates of the crust to move around forming mountains and volcanoes as they collide or move away from each other.
- The crust made up mostly of silicon and oxygen (the crust is thinner under the ocean than the rest of the crust).
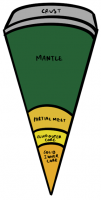
The Moon
- Similar to Earth in composition but no longer has volcanism as there are no plate tectonics.
- The composition is so similar because they were made from the collision between a small planet and the Earth and the moon was the bit left over.
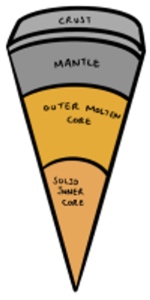
Mars
- Mars has a solid inner core made of dense iron, nickel and sulphur.
- It has a rocky mantle and a crust mostly made of iron, magnesium and aluminium.
- Previously it had tectonics which formed volcanoes and the largest canyon in the solar system (Valles Marineris).
- It also has similar sedimentary processes to Earth such as dunes.
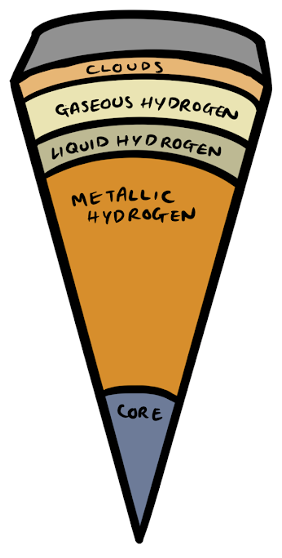
Jupiter
- One of the gas giants mainly made up of hydrogen and helium.
- Structure similar to the sun. It is unclear what the core of Jupiter is made up of, but it is surrounded by metallic hydrogen formed when the hydrogen is under so much pressure that the electrons are squeezed off making it electrically conductive like metal. The upper layers of Jupiter are then more hydrogen either as a liquid or gas (the high pressure and high temperature makes the hydrogen a liquid).
- Jupiter spins so fast that it generates a magnetic field.
- It has 63 moons, one of which is Europa:
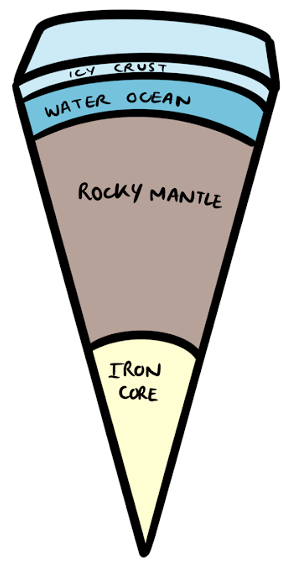
Europa (a moon of Jupiter)
Europa has an iron core, a rocky mantle, an ocean of salty water, and a lot of ice.
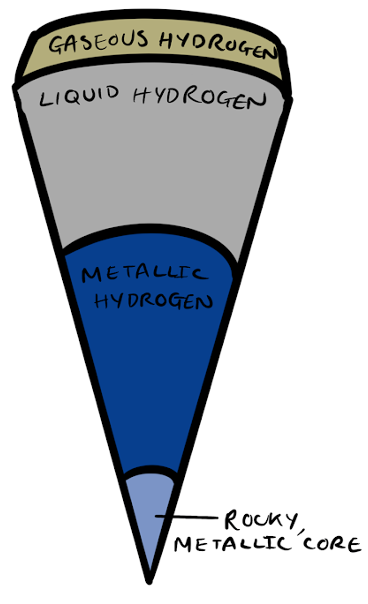
Saturn
- Another gas giant mostly made of helium and hydrogen.
- Saturn’s core is made up of dense metals like iron and nickel and some rocky material.
- Saturn’s density is less than water which means it could theoretically float on a giant mass of water.
- Saturn is the only one of the gas giants with visible rings as the rings are mostly made of ice which reflects the light well.
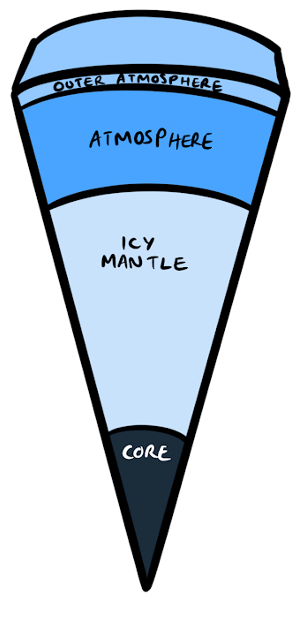
Uranus
- This ice giant rotates at nearly 90o from the plane of its orbit, which makes it look like it’s spinning on its side.
- The icy mantle surrounding the small rocky core is made up of dense water, methane and ammonia.
- The atmosphere is made up of methane gas which give Uranus it’s blue-green colour.
- It’s bigger than Neptune but it has a smaller mass.
- It has 27 moons.
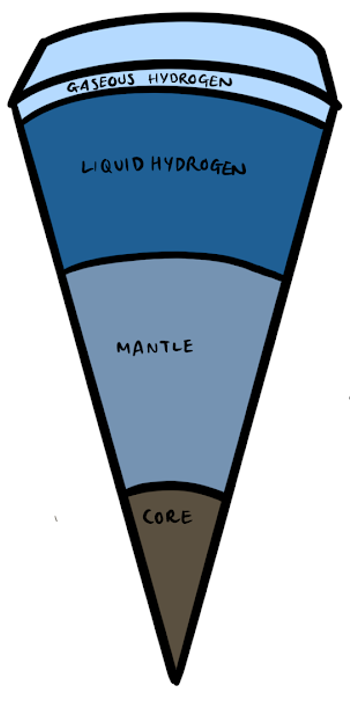
Neptune
- Neptune is shrinking and releasing heat.
- It has a similar structure to Uranus as its mostly made up of icy materials made of dense water, methane and ammonia fluids around a small rocky core.
- It’s atmosphere is mostly made form hydrogen, helium, and methane and it doesn’t have a solid surface (similar to all of the gas giants.)
- It has 14 moons.