There is a huge shortfall of ICT professionals worldwide, with many companies looking to increase the number of women working for them. However, many girls don’t even consider a career in ICT. We decided to celebrate some influential women in ICT from the times computers were invented to now.
Ada Lovelace
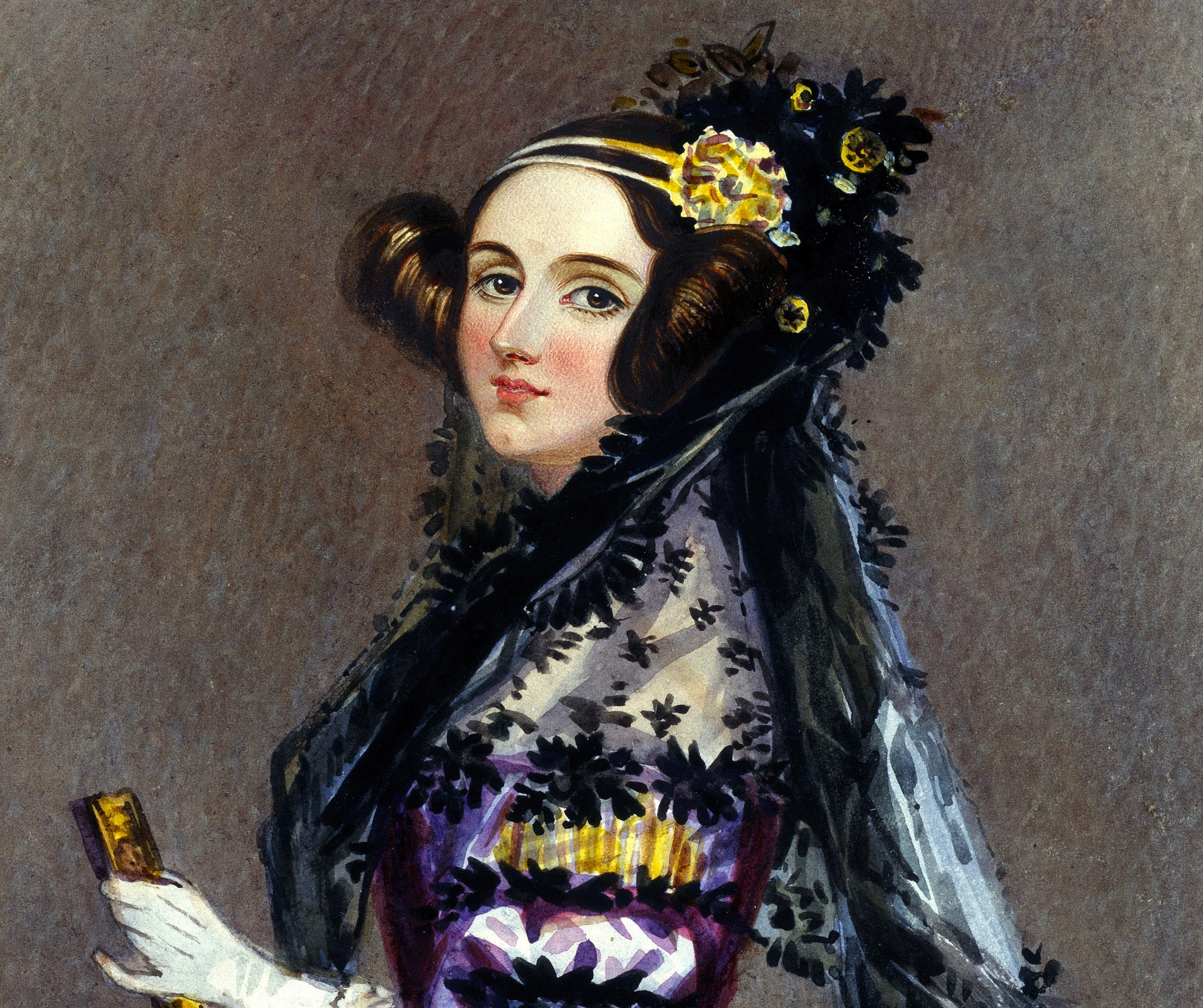

Ada was an English Mathematician who worked on the ‘Analytical Engine’, one of the first designs for modern computers. She recognised that computers could do a lot more than was previously thought and designed the first algorithm that could be carried out by computers. She is often called the first computer programmer for designing this.
Joan Elisabeth Lowther Murray

Joan was an English cryptanalyst (analysing information systems to breach cryptographic security systems) who is best known for her work as a code breaker at Bletchley Park during World War II. She worked on the Enigma project, which cracked the German system of encoding their messages and led to WWII being much shorter and saving thousands of lives. The Enigma project was a very early form of ICT.
Grace Hopper

Grace was an American Computer Scientist and a United States Navy Rear Admiral. She was the first person to develop a compiler, despite being told by many people that it would never work. A compiler is a programme that changes what you write on a computer into a language that can be understood by the computer. This allows computers to work with words rather than just numbers as was previously done. There is now a yearly Grace Hopper Celebration of Women in Computing, giving women in computer science a chance to share their research.
Anita Borg
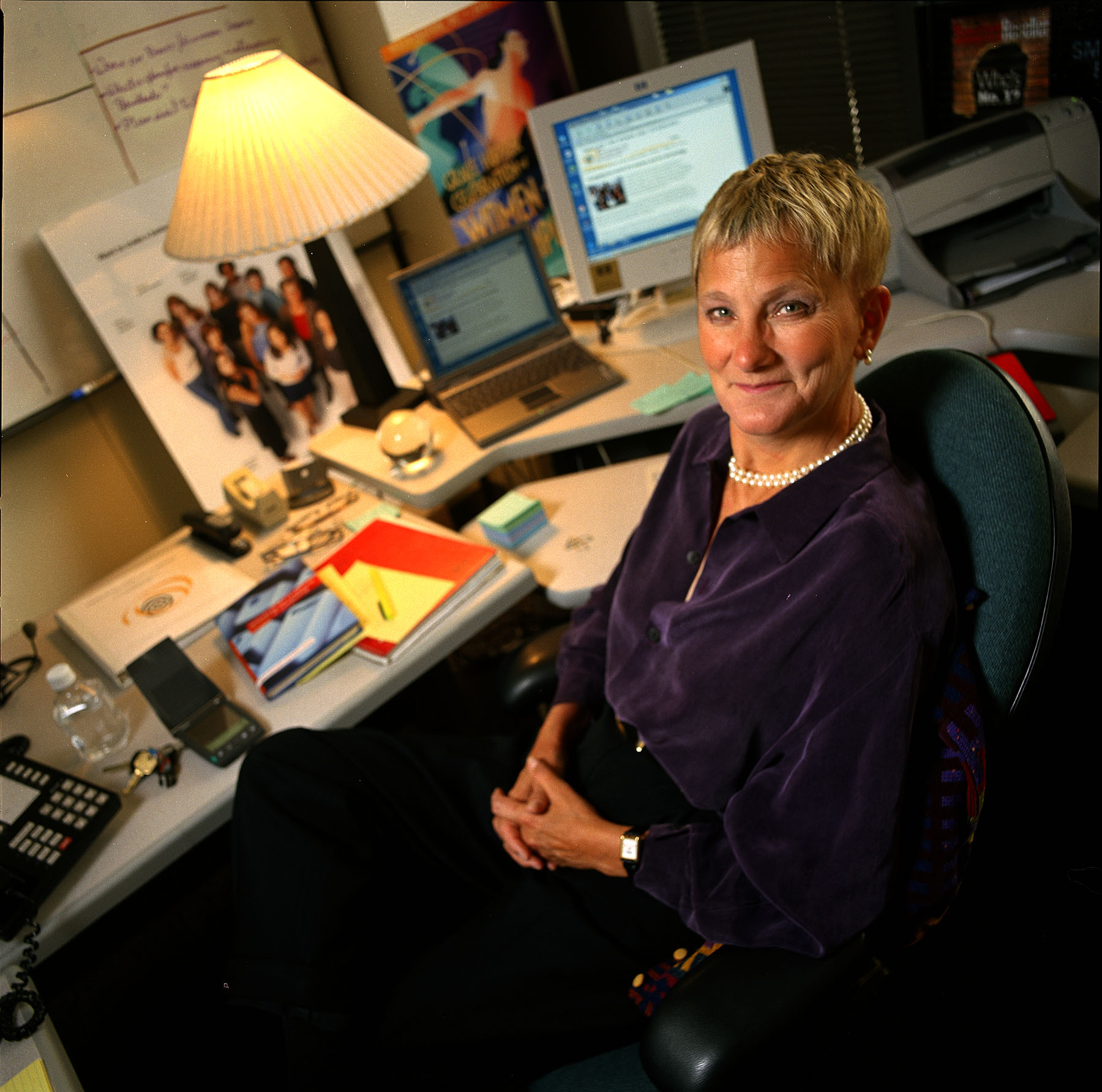

Working as a computer scientist she developed ways to analyse high speed memory systems in computers. She founded Systers, a network for women in technology, and the Grace Hopper Celebration of Women in Computing. In 1997, she founded the Institute for Women and Technology (now the Anita Borg Institute), to increase the number of women in technology and their impact on the world.
Marissa Mayer
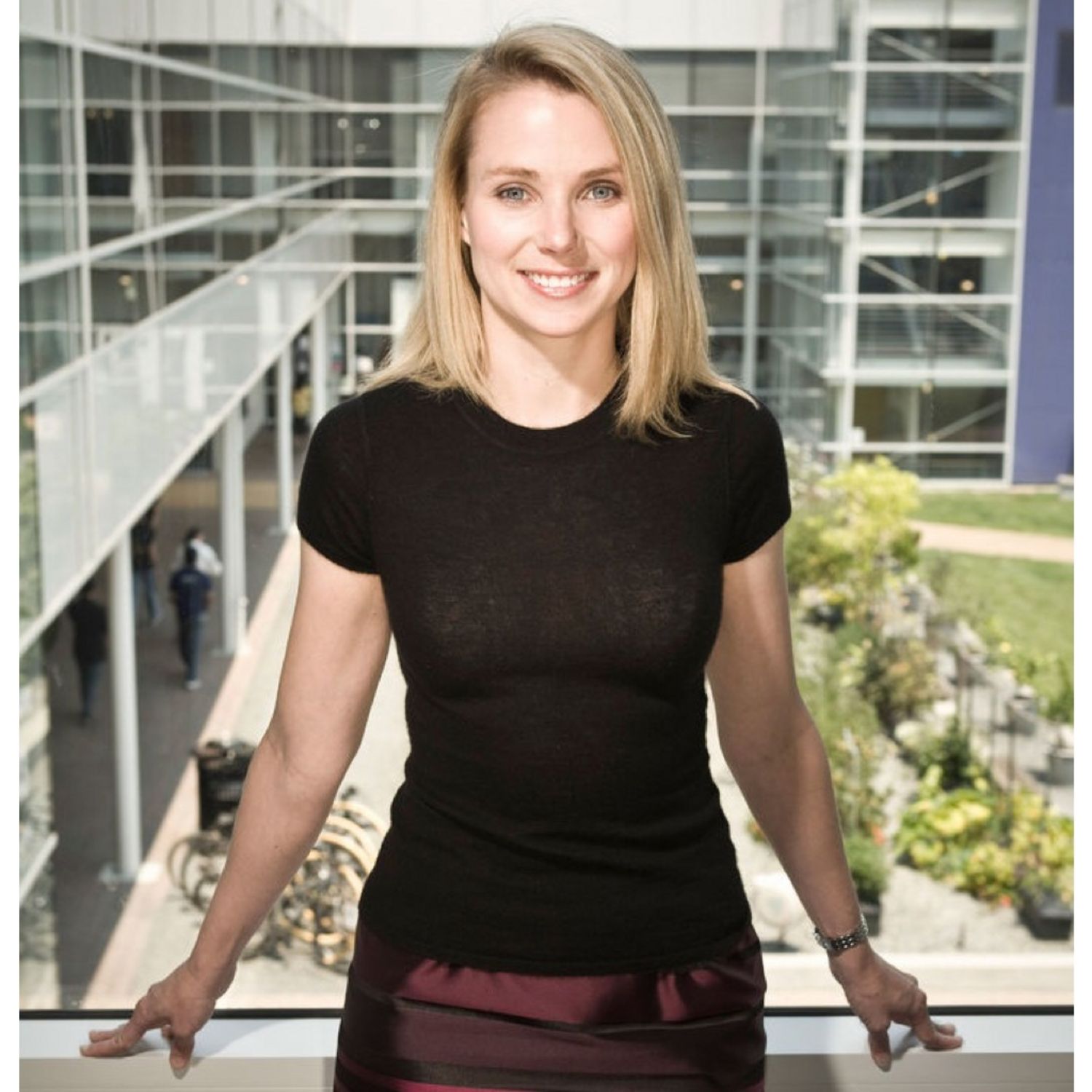

She joined Google as employee number 20 and as their first female engineer after studying computer science at university. She oversaw the layout of Google’s home page and became Vice President of search products and user experience. In 2012 she became president and CEO of Yahoo! and led them to buy Tumblr in 2013.