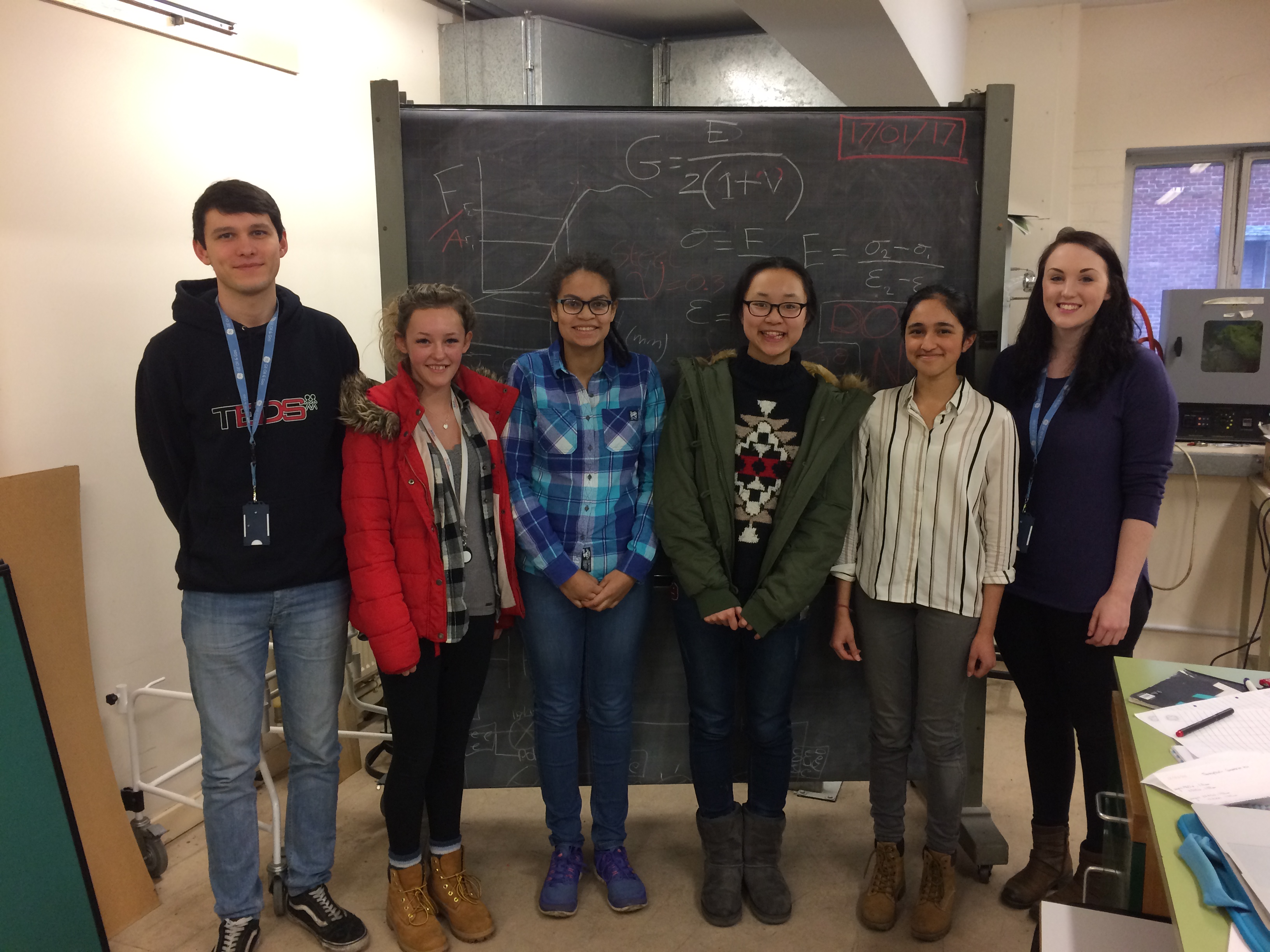
This week we’ve been helping out with the Engineering Education Scheme. Lots of year 12 students from the local area have been working with industry to come up with a project based on real scientific, engineering and technological problems. The students have come in and had a chance to work in the engineering laboratories and workshops that university students and researchers would use. After lots of problem solving and hard work, they presented what they had done so far. These are just a selection of some of the projects.
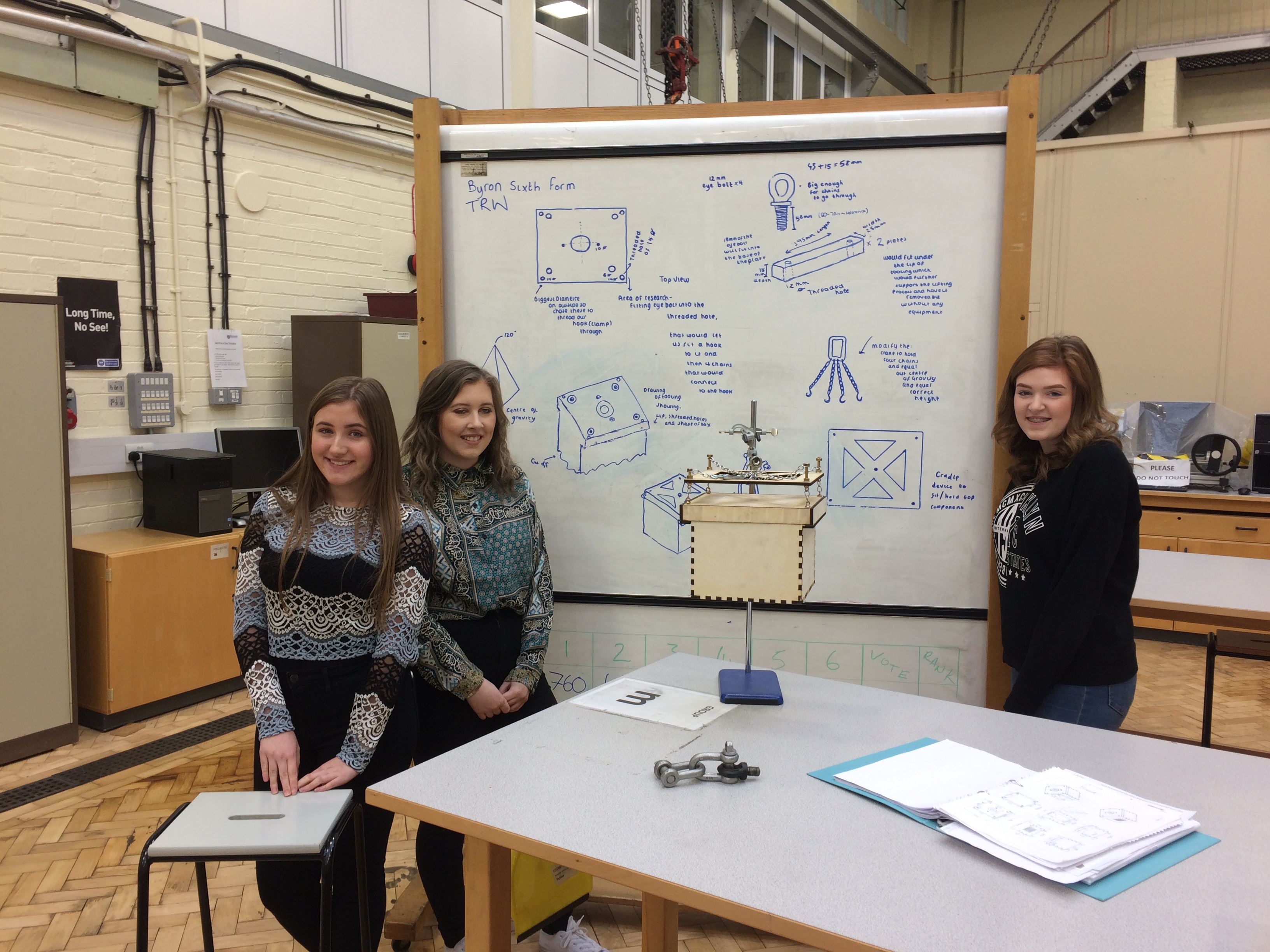
Mechanical Engineering – Lifting
This group was working on creating a lifting mechanism for a heavy item/box. The current method of lifting isn’t very good as its centre of gravity is in the middle so it wobbles when they lift it. They created a design with a cradle for the box which spreads out the centre of gravity. It is more stable and quicker to lift, saving the company time. The use of shackles mean the box can attached by hand, no tools are needed, again saving time.
Mechanical Engineering – Shield
A mechanical engineering group created an extendable shield. This is important for keeping people safe in war. In general all shields appeared to be really big or small, but there were none that could adapt to the situation. Use of cogs allowed the shield to be extended or retracted, solving the problem.

Electrical and Civil Engineering – Solar Power
The brief from WSP Global was to provide renewable energy through use of solar panels to the 350 people who work in the office. The students made a to scale model of the office based on blueprints and used a fixed angle light (as the sun) to look at the shading on the roof of the building. They also ran computer simulations to look at which areas would capture the most sun.

Civil Engineering – Leisure Centre
The brief was to design a leisure centre on land near to St James Football Park. There were lots of problems to be overcome in the design. The centre was to be built on top of an old mine shaft, which might mean the building would fall into the ground. They calculated that it was too expensive to fill the land underneath with concrete, so calculations had to be made for how heavy each part of the leisure centre would be.

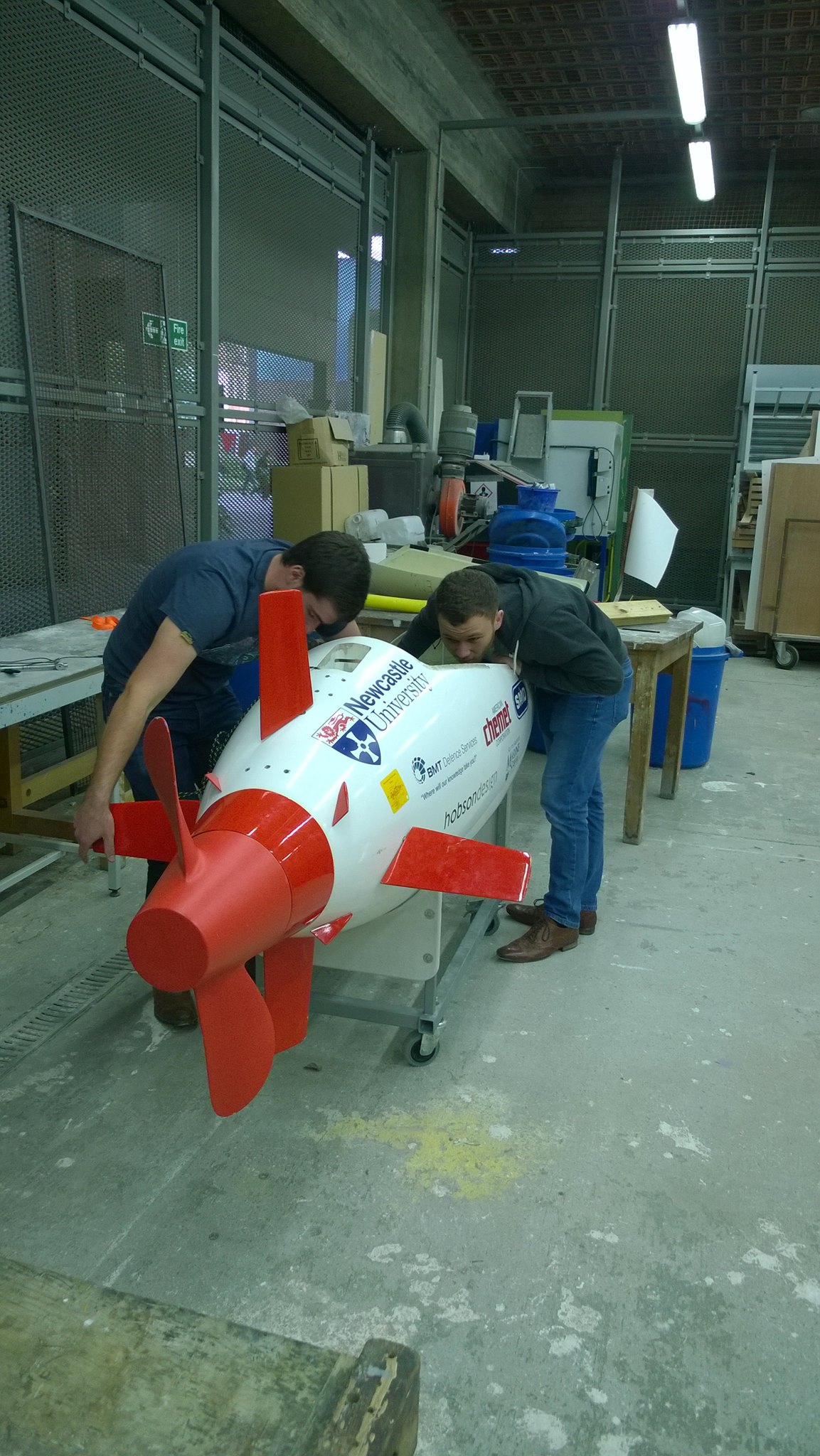
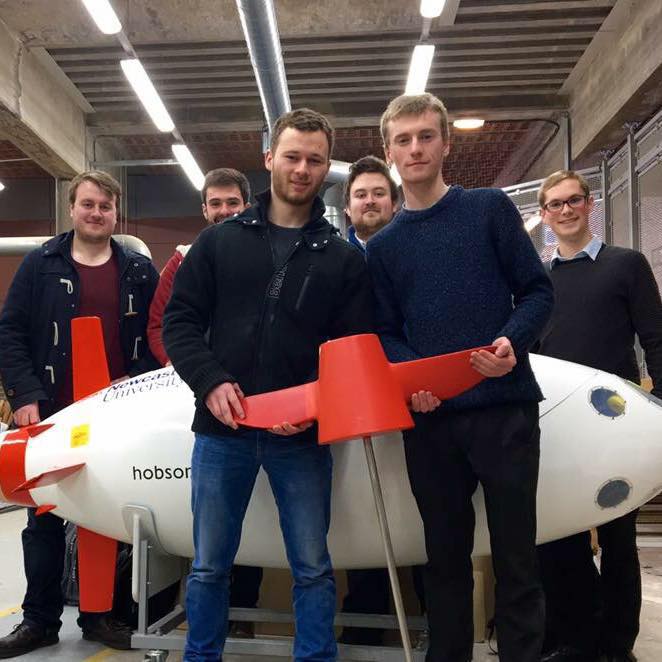
Marine Engineering – Underwater vehicles
This marine engineering group was helped by engineers from BAE systems. They looked at making an underwater unmanned vehicle. They had to do some problem solving with getting the submarine to sink, working out the exact amount of weight required to make it neutrally buoyant. They used electromagnets to power the vehicle.


Marine Engineering – Underwater pipes
This group worked with GE oil and gas looking at using flexible pipes underneath the seabed. They compared two different materials; thermoplastic and thermoset. They did lots of tests, looking at things such as compression (squashing) and torsion (twisting) to find out its properties. They also looked at factors such as the price. Testing found that it was really important that there were no faults in the thermoplastic as it broke a lot easier. Underwater pipes are really important for transporting things like oil and gas.







