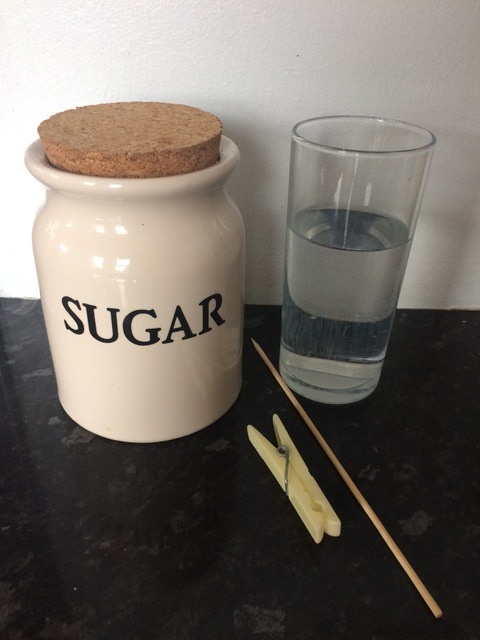
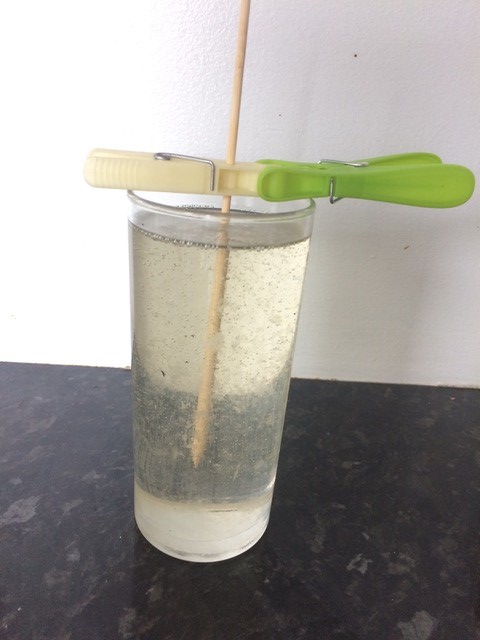
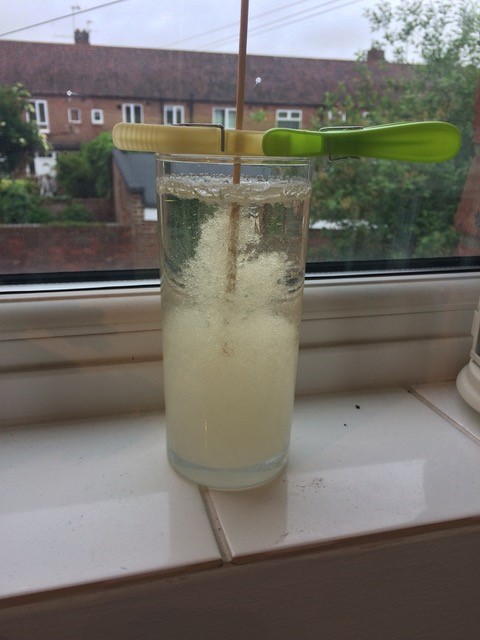
As we have reached the end of the school year, here is a little round up of some of our favourite questions that children have asked us during STEM workshops.
1. Why doesn’t the energy ball give you an electric shock?
The energy ball is a little device we have that looks like a ping pong ball with two metal strips on top. Inside there is a light, a buzzer and a battery. If two people touch one metal strip each and then with their other hands touch each other, the ball lights up and buzzes. This works because we are conductors of electricity – electrons from the battery flow through us and back into the ball to complete the circuit.
The reason you don’t feel a shock when touching the energy ball because there isn’t enough electricity flowing through you to be able to feel it, and certainly not enough to harm you!

2. What do plants poo and wee? – St Wilfrids, Blyth
All living things have seven things in common – movement, respiration, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, excretion and nutrition. The sixth one, excretion, is a scientific word for producing waste. In humans, and many animals, that is our poo and our wee. They are the leftover waste products that our body doesn’t need so gets rid of.
Plants are living things, just like us, but you may have noticed they don’t poo or wee like we do. Rather than eat food like us, they make their own through photosynthesis. This produces a waste gas called oxygen which we breath in. Plants excrete oxygen rather than poo or wee.
3. Why does the moon control the sea? – Grange First School
Gravity is the force that keeps us close to the Earth, all really big things like planets and stars have a gravitational pull that attracts things near by. Because the moon is so big and so close to Earth it has quite a strong gravitational pull on our planet. The moon causes the water in the oceans facing it to pull towards it, resulting in a high tide. The pull of the sun’s gravity and the Earth’s own gravity also have an effect on the tides.

4. I’m the only one who can touch their nose with their tongue, is that because of my genes? – St Marys, Jarrow
Touching your nose with your tongue is known as Gorlin’s Sign. It is associated with a genetic disorder but not everyone that can do it has the disorder. About 10% of people without the disorder can touch their nose with their tongue and it does not appear to be due to genes you have inherited from your parents.
5. Why do we get goosebumps? – Billingham South Community School
We often get goosebumps when we’re cold, but they don’t do much to help us warm up, so why do we get them? Before we evolved to be modern humans, our ancestors were much hairier, we they got cold, getting goosebumps would cause their hairs to stand on end. As they had much more hair than us, they were able to trap a layer of air in the hair by doing this, providing them with extra insulation to keep them warm.
Although goosebumps are no longer helpful to us, we haven’t lost the trait through evolution because it doesn’t harm us. Therefore if a person was born with a mutation in their genes meaning they didn’t get goosebumps, they wouldn’t be at an advantage because of it so the non-goosebump genes wouldn’t necessarily be passed on more than the goosebump genes.
If you have any STEM related questions that you would like us to answer, just leave a comment in the box below!