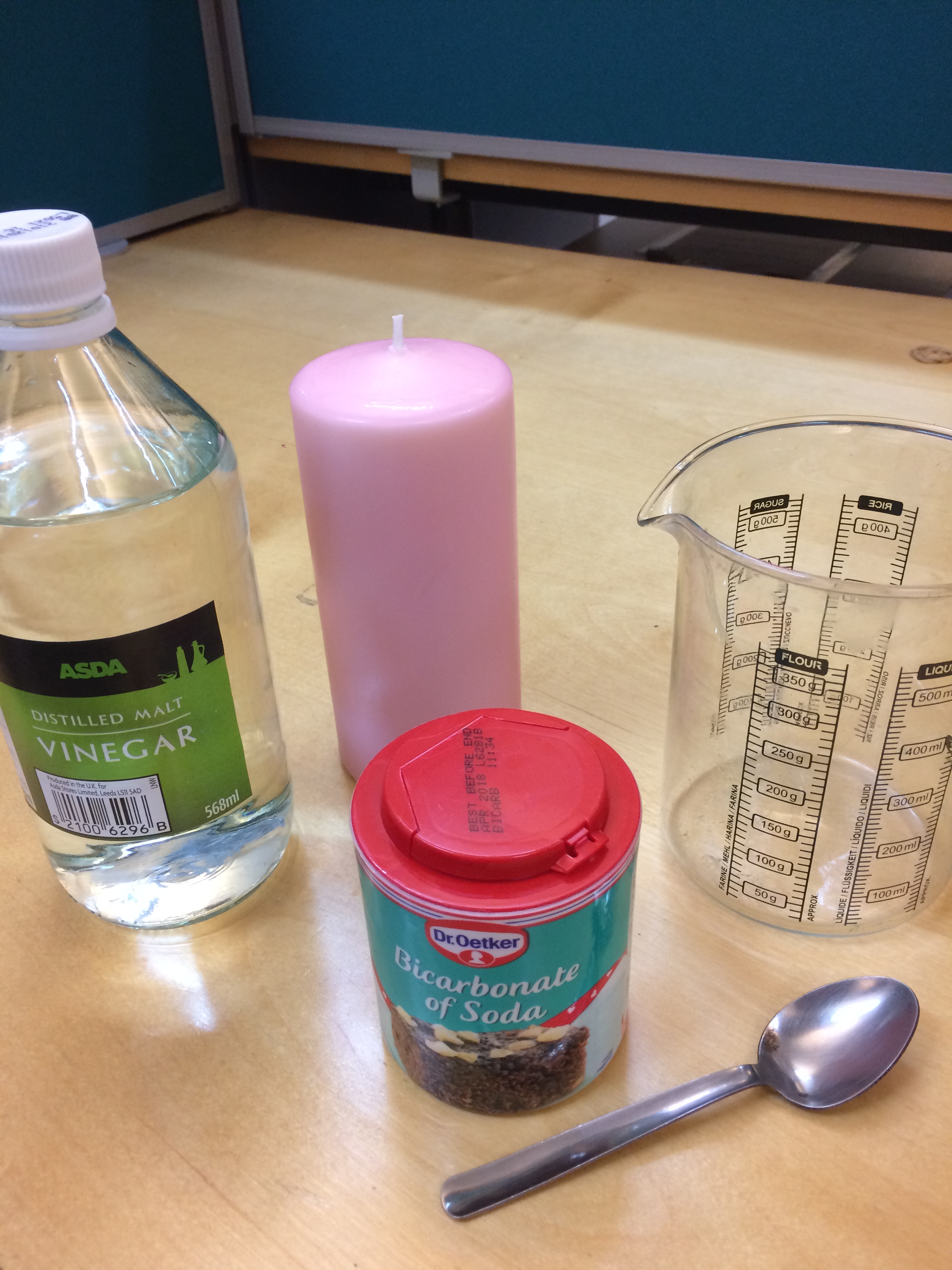
For this experiment all you will need is a clear bottle or jar with a lid, water, cooking oil and some washing up liquid.

Fill the water bottle half full with water.
Pour about 100ml of oil in to the bottle and observe what happens.

The oil should float on the water. Try and mix them together or challenge other people to mix them! It is impossible, the oil and water always separate out again.

Add a squeeze of washing up liquid to the bottle and shake. The oil and water now mix together.

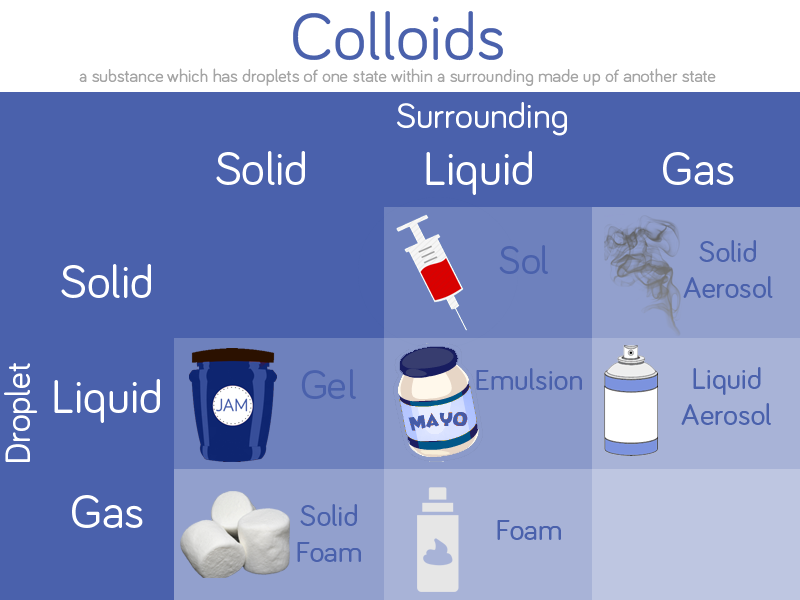
The Science
Oil is less dense than water so floats on top. Oil and water don’t mix together as the water molecules are more attracted to each other than the oil molecules. Oil molecules are hydrophobic or ‘water-fearing’.

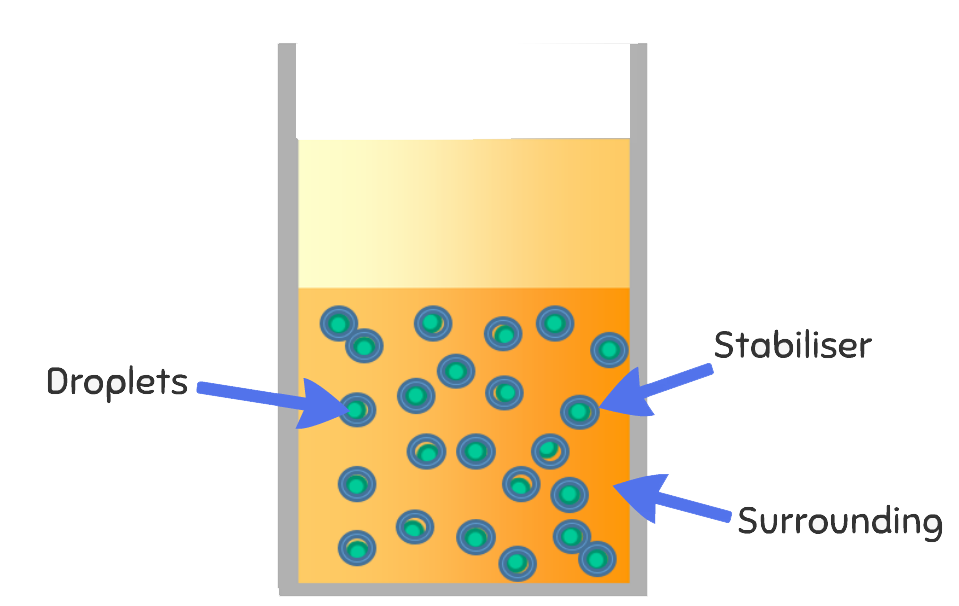
Washing up liquid molecules are attracted to both water and oil. When you add a squirt in, one end of the washing up liquid molecule attaches to a water molecule and the other end attaches to an oil molecule. This creates a mix of water with oil droplets spread throughout it. This is because one end of the washing up liquid molecule is hydrophobic (water fearing) and one is hydrophilic (water loving).
The washing up liquid acts as a stabiliser and creates an emulsion. This is a mixture of two liquids that wouldn’t normally mix.
Real Life Applications
We use washing up liquid when we are washing up as it attaches to the oil on the dirty dishes and lifts it off into the water.
Animals that live in the ocean also stay warm by producing an oily substance on their fur or feathers which keeps the cold water away from their skin.








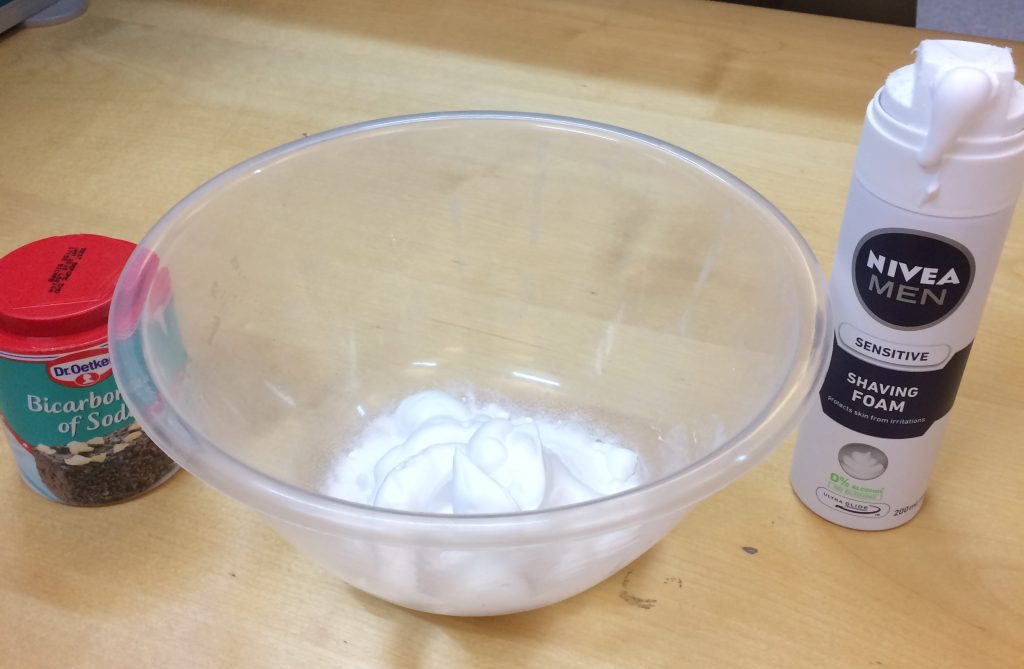
 1. Add 4 teaspoons of bicarbonate of soda to the glass
1. Add 4 teaspoons of bicarbonate of soda to the glass