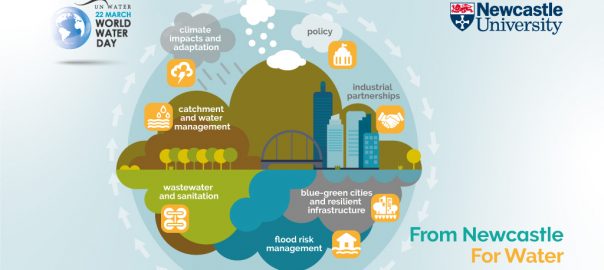
In this post, Brett Cherry – our Writer in the Lab blog author, talks about the global water challenges we are facing and how Newcastle University is tackling them.
The challenges we face for water are similar if not more critical than that of energy. While both are necessary to survival, water is even more essential to life especially clean water. Access to clean water and sanitation is largely taken for granted in richer countries, while the vast majority of the world’s population struggle to live without them.
But even the UK, where it is often quite wet is threatened by water shortages in the future, indeed some parts of the country have already experienced them and will likely continue to. The main pressures here are climate change which will result in water shortages due to drought and a population increase of 8 million people by 2050.
Think for a moment that while many of you reading this will have access to a working toilet, over 2.3 billion people do not have such a luxury. The consequences of inadequate sanitation are many, not to mention deadly. 1800 children die every day from poor water, sanitation and hygiene.
The challenge for us in the ‘more developed’ world is to find solutions that are not merely scientific, technological or even economic, but also social, educational and governmental. Enter the Water Security and Sustainable Development Hub that brings together 94 organisations from 25 countries to tackle challenges around water security.
Water security for all
If we are to make sure that no one is left behind in making available clean water and sanitation for all then we must work together to achieve this. No single university, government, industry, NGO or individual will be able to do this alone. There are of course obstacles in collaborating with those whose objectives and values may slightly differ, but the stakes are simply too high not to.
Sometimes working together may be easier than originally thought, as the questions from one field may be answered by an entirely different but related one. If authorities ask why a population behaves or acts in a certain way, social scientists or NGOs may be best placed to answer.
The solution is simple: make provisions for clean water and sanitation available to those who need them. But the answer to ‘how do you do it?’ may be far from simple. Similar to the problem of making energy low-carbon, there is no one way to make clean water and sanitation a global reality.
If a community needs a low-tech, low-cost approach to supplying or storing clean water, engineers may have a solution for them. If knowledge of it needs to spread throughout the community then education will be involved. If national policies are needed for it to be adopted in a uniform way across the country, then it involves governance.
The Water Security Hub aims to work in an interdisciplinary way that cuts across disciplinary, national and professional boundaries. It is looking to highlight and enable hidden voices, such as young people, to be heard as they are one of the main stakeholders for SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation.
For more info about the Water Security Hub check out this podcast:
https://soundcloud.com/user-634032444/ukri-gcrf-water-security-and-sustainable-development-hub-part-1

Wastewater and sanitation
The impacts of poor wastewater treatment and inadequate sanitation have already had global knock-on effects. After all it should come as no surprise that the combination of concentrated populations in cities, for example, with little to no sanitation, dramatically increases the risk of antimicrobial and drug resistance. It also spreads.
Numerous studies from researchers, such as Professor David Graham and colleagues at Newcastle University, have repeatedly shown from their field work that microbial resistance to antibiotics is spreading from regions of the world with high populations, but little to no adequate sanitation facilities like toilets.
As announced late January, AMR genes have been found in the High Arctic, what many would consider one of the last pristine environments on Earth. But as this and other research has shown, there are few if any places in the world that have not been touched by human influence.
To stop the global spread of antimicrobial resistance the world must work towards Goal 6 everywhere. The health and welfare of local communities and the wider global community depends upon it.

Flood risk management
While some parts of the world struggle with not enough water, others struggle with too much water. Water giveth life and taketh away. It is a force of creation as well as destruction. Similar to wastewater and sanitation, managing flood risks also must involve a holistic approach.
Flooding in urban and rural areas alike leads to incredible damage to life, property and livelihood. In the UK the cost of flooding is around £2.2 billion per year. But there are now tools for modelling and better understanding flood risks that enable cities and rural areas to mitigate or at the very least learn to live better with flood hazards.
Flood research at Newcastle University employs high resolution, integrated models for flooding that include the influence of climate change. Climate affects flooding in a big way. In the summer climate change intensifies short bursts of rainfall known as ‘convective storms’ (intense showers formed by rising air).
Forecasting tools integrated with high resolution climate models make possible more accurate forecasts, and modelling the movement of water through a sewer system leads to more accurate simulations of flooding. Not to mention ‘digital twin’ technology which has the potential to create a real-time digital replica of an entire city. This makes it possible to prepare in advance and manage flood risk more effectively.

Climate impacts and adaptation
Climate hazards are numerous throughout the world. They include not only floods, but droughts, heat waves, storms and other extreme weather events. We need to ask the question ‘how much more likely are these events under a changed climate?’ to get a more accurate picture of how climate change affects us.
To improve forecasting research led by Professor Hayley Fowler and colleagues, uses high-resolution climate scenarios that scale down these extreme events to the local areas they impact. All of this work is about improving adaptation to climate change.
Climate change has major implications for infrastructure, such as energy, water, health care and transport. We need to understand also how these different infrastructures are interdependent, for example how a major power outage affects health care infrastructure like hospitals, or blocks emergency services.
Shortages in water affect energy services as it is used to cool down power plants. For these and many other reasons climates risk should be factored into infrastructure planning.
In a recent speech given by Sir James Bevan, Chief Executive of the UK Environment Agency, he says all water companies in the country ‘identify the same thing as their biggest operating risk: climate change’. This means we need infrastructure that can act as a water sink as well as a water supply, a reason to make infrastructure ‘blue-green’.
Blue-green cities and resilient infrastructure
Green walls, rain gardens and permeable surfaces that serve as buffers for rainwater are examples of ‘green’ infrastructure. Ponds, pond systems, leaky dams or water courses that store water on the surface are forms of ‘blue’ infrastructure. Put them together and you have ‘blue-green infrastructure’.
Blue-green infrastructure is potentially an important tool for allowing cities to adapt to climate change. It also can improve air quality and enhance ecosystems.
Newcastle University research on blue-green cities spans modelling, monitoring and demonstrating blue-green infrastructure. The National Green Infrastructure Facility, led by Dr Claire Walsh and Dr Ross Stirling, based at the Urban Sciences Building at Newcastle Helix, evaluates the benefits of blue-green infrastructure. An important part of this research is using digital sensors to monitor say how much water a tree stores or a swale.
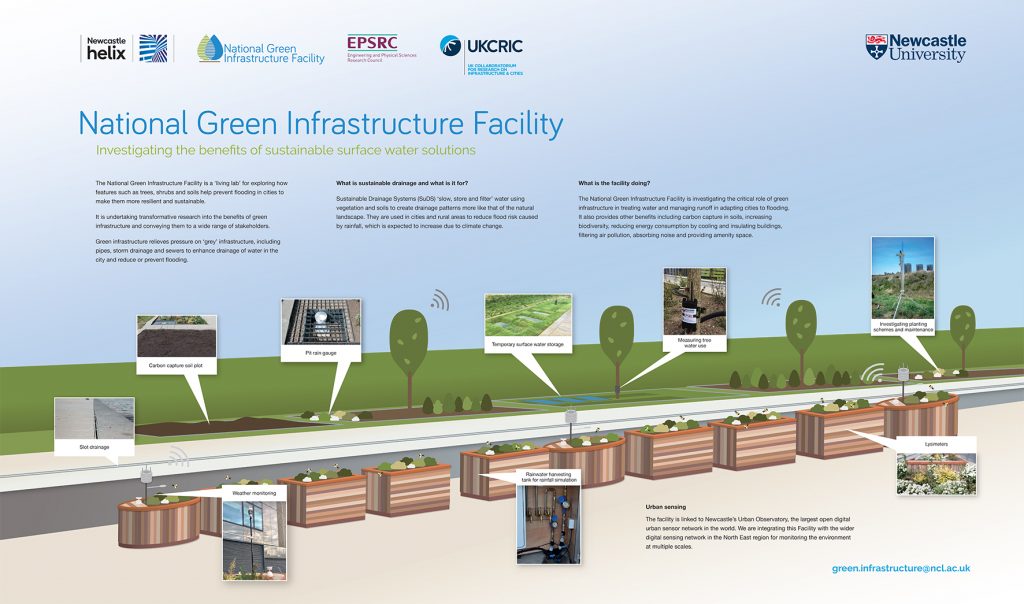
While there are many good reasons for using blue-green infrastructure in cities, testing them with science makes possible new innovations that may not have been known or made possible before. To make cities resilient to flooding means overcoming any existing barriers to sustainable flood mitigation. Cities are also part of a wider water catchment that should be taken into account.

Catchment and water management
A water catchment is the area where water is collected in the landscape and drains into a water body or course such as a lake or river. Whether in the countryside, the city or somewhere in between we live and interact with a water catchment, although the ways in which water travels through the landscape may radically differ as cities have mainly paved surfaces.
In rural catchments much of the research from Newcastle has focused on ‘natural engineering’ approaches to slow, store and filter water. This means working with the landscape to mitigate flooding and combining multiple sets of expertise from science and engineering to social science and knowledge of local communities.
Most of the problems of flooding and drought are due to enhanced loss of water from the landscape. This means finding ways to retain water within the landscape makes it possible to manage the catchment in an integrated way that takes into account ecosystems and communities.
The programmes of research at Newcastle University on water are many, to discover more visit the Global Challenges Academy’s website.