Before you can start writing effective web content you need to be clear about what you’re trying to achieve with your site and who your main users are.
For every page you plan, ask yourself:
- Why am I creating this page?
- Who am I creating this page for?
- What do I want the user to do after reading it?
People generally come to a site to find something out so it’s important that you answer their questions with your content.
Once you know the messages you need to communicate and who you’re communicating them to, you can start prioritising content.
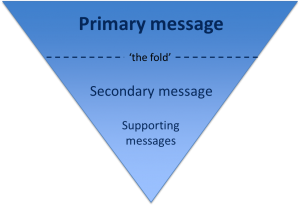
The fold
‘The fold’ is a term used in web development to refer to the point on a webpage where people need to scroll.
Amy Schade (Nielsen Norman Group) in The fold Manifesto: Why the Page Fold Still Matters explains that people will only scroll if content ‘above the fold’ appears relevant to them. So it’s essential that web content at the top of your page is an accurate indicator of what information appears further down the page to encourage users to scroll.
This is a really useful concept to bear in mind when structuring content on your webpage.
The inverted pyramid
It’s also helpful to think about structuring a webpage in the same way that journalists structure a news article – by using the inverted pyramid.
The inverted pyramid is the idea of turning a story on its head. You start with the key point and then provide more detail further down the page. This ensures that essential information is at the top of the page. This is vital for mobile devices as a smaller screen size means that less content will appear ‘above the fold’.
Karen McGrane in her book, Content Strategy for Mobile, recommends thinking about your primary, secondary and supportive messages to help prioritise content on a page.
Primary message
Your primary message is the main point of the page. This should be communicated through your page title and introduction so that users can quickly see what the page is about.
Page titles should be clear and descriptive so that users can understand them at a glance. Similarly, your introduction should be concise and engaging. It should also contain key words for search engine optimisation. The introduction should summarise the main message in 50 words or less to grab the reader’s attention and encourage them to scroll down the page.
Secondary message
The secondary message is the body copy of your page. It expands on your main message and provides more detail. The body copy should answer your users’ questions and be concise and scannable.
Supporting messages
The supporting messages are qualifiers and additional information to support your main messages. They can include quotes, images and videos. Supporting messages can also provide a next step, such as a call to action like booking a place at an event or taking a virtual tour.
Summary
People spend less time reading online and will only scroll if they think that information further down the page will be useful to them. It’s vital to prioritise content so that your primary message is easily visible. Structuring content effectively is therefore fundamental to ensuring your main message is conveyed to your users.
References
Amy Schade, The fold Manifesto: Why the Page Fold Still Matters, Nielsen Norman Group, 1 February 2015
Karen McGrane, Content Strategy for Mobile, A Book Apart, 2012
Jakob Nielsen, F-Shaped Pattern For Reading Web Content, Nielsen Norman Group, 17 April 2006