Readability for websites isn’t just about people understanding the words, although of course that’s a massive part of it.
After all, if you can’t understand what the words are trying to tell you, you’ll just leave the site without the answers to your questions.
We’ve proven it time and time again – the readability of complex information can be improved by using clear, easy to understand English. It’s just making sure more people can understand it.
What I’d like to focus on for this post is some tips about the other elements that can affect readability; prioritisation of content, page layout, the use of design, and ease of navigation.
Prioritisation of content
What is it that people really need to know about on your page? If you identify it, you can prioritise the content to improve readability. Content should always be created and designed with the user’s needs in mind.
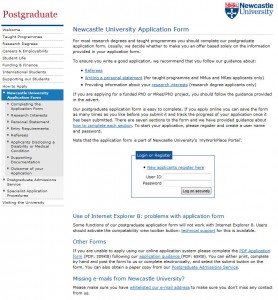
For example, here’s a screen shot of the old version of the postgraduate ‘How to Apply’ section. It had low readability; complex information, use of jargon and too many words! Your eye is also drawn to the box in the middle of the page, which was a little distracting.
We reviewed the section, identifying the purpose of the content (get people to apply) and got to work editing.
We use page titles to help accurately introduce the content for people. A change of title from ‘Newcastle University Application Form’ to a very clear ‘How To Apply’ certainly helped…
Also, editing reduced the content from 12 to just four pages.
Another way we have improved readability is to use introductions on pages. This ensures people can quickly read a descriptive summary of the page. Take a look at Linda’s post about how to write great introductions.
Page layout
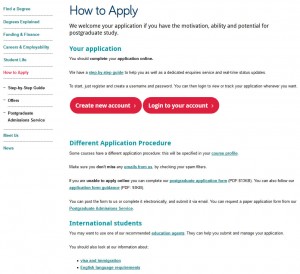
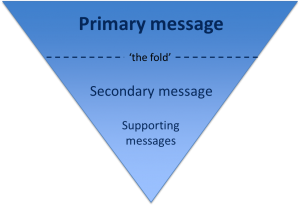
We reviewed the page layout or format, quickly deciding a step-by-step guide would be most effective at helping people though the application process. We even added a relevant video to support our primary messages.
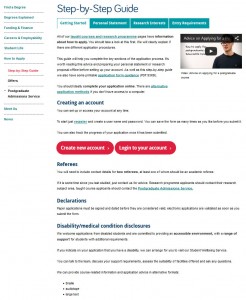
Pages of content were re-worked into a simple step-by-step guide using tabbed content (select to view expanded image)
Use of design
We’ve blogged before about how design can help people navigate around your site, but it can also help draw attention to key content/things you want people to do. And no…I’m NOT talking about flashing animation here, but more subtle design devices.
I’ll explain – we often use expandable boxes on pages to hold content for specific audiences. It’s so that content can be seen – but doesn’t have to be opened unless it is relevant to you.
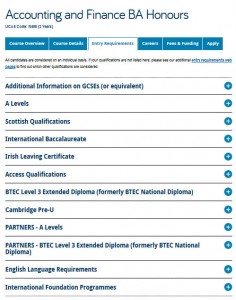
We use expandable content on the Undergraduate website for a long list of entry requirements, see the screen shot below. Don’t panic at all the options! Relax and simply choose the content relevant to you…
Test, test and test again
We’ve tested the content on the new postgraduate application pages using Clarity Grader (a website content analysis report) and the results are really positive:
Readability has increased from 48 to 55 (we aim for 60).
Long sentences (harder to read) were at a whopping 19.69% before we re-developed the page and have decreased to 7.97% (we aim for 5%).
This is all the more impressive when you consider the content is mostly complex and detailed information on application procedures.
Final tip
One of the key things to remember – is that you can always go back to pages and improve readability. It might be a slight tweak to a sentence, or a layout change – the main thing is that you can always improve it.
We ran some extensive testing on the postgraduate content. After all, a lot of what we did, not just to the content, but to the layout and design, then formed the master plan for Go Mobile – so it needed to be right. Did we do it?
Oh yes. You can read about the excellent results in an earlier post of mine. A particular favourite is the below word cloud created from user feedback about first impressions of the postgraduate website. The most popular words that users used to describe the site included: easy, simple and clear.
Go on, take the challenge – have a go! Choose one of your pages and see how you’d improve readability. I’d love to hear what you get up to!