As many ICaMB members will have been aware, we have been very busy this year recruiting a new generation of Principal Investigators (PIs). New faces bring new ideas and fresh perspectives and we are very excited to have successfully identified and then persuaded a number of talented scientists to join us in Newcastle. In addition, we congratulate Yulia Yuzenkova, one of our current postdocs, for winning a prestigious Royal Society University Fellowship.
Independent Researcher Establishment Scheme (IRES)
For our new IRES fellowships we sought to identify three new PIs in any area of research that fitted within the broad interests encompassed by ICaMB. These awards are for a 5-year period and, after review, are intended to lead to a permanent academic position in our Institute. The new IRES fellows will be expected to establish an independent research programme and obtain the funding to build a research group. We received many high-quality applications for these positions and the competition was very intense. We are very happy, therefore, to welcome our three IRES fellows and look forward to them being our colleagues for many years to come.
Dr Owen Davies
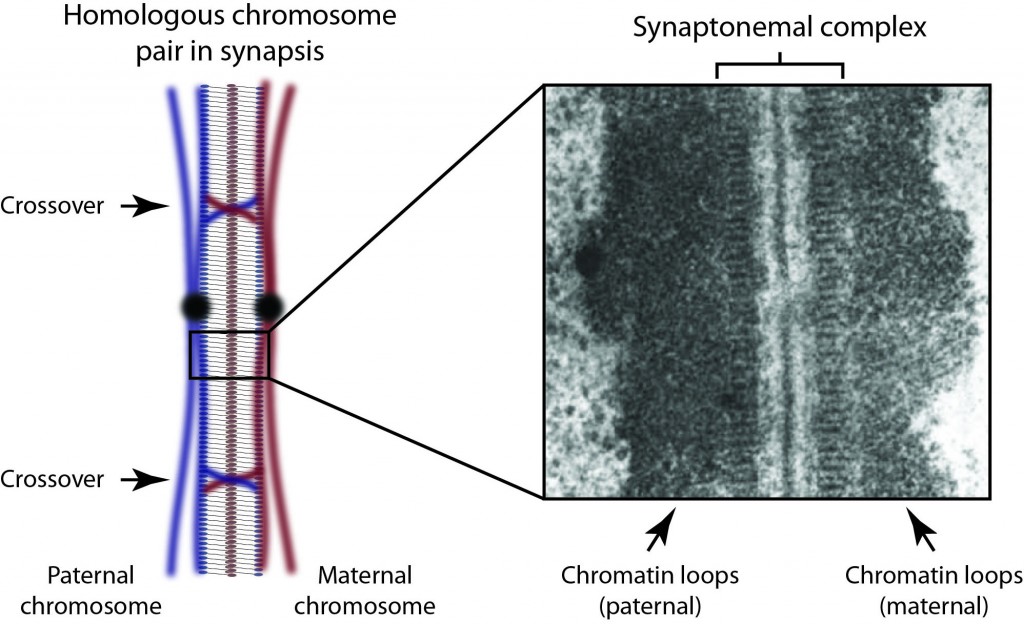
 Research Interests: The synaptonemal complex is a giant molecular ‘zipper’ that binds together homologous chromosome pairs along their entire length during meiosis. It is essential for meiotic recombination, crossover formation and fertility. Despite its discovery almost 60 years ago, we still lack any information regarding its molecular structure and function. My research is directed towards overcoming this knowledge gap and defining the full three-dimensional structure of the human synaptonemal complex together with the molecular basis of its function in meiosis.
Research Interests: The synaptonemal complex is a giant molecular ‘zipper’ that binds together homologous chromosome pairs along their entire length during meiosis. It is essential for meiotic recombination, crossover formation and fertility. Despite its discovery almost 60 years ago, we still lack any information regarding its molecular structure and function. My research is directed towards overcoming this knowledge gap and defining the full three-dimensional structure of the human synaptonemal complex together with the molecular basis of its function in meiosis.
Background: After my PhD, I secured a post-doctoral fellowship from the Royal Commission for the Exhibition of 1851, which I took to the Institute for Stem Cell Research, University of Edinburgh. There I worked with Dr. Sally Lowell studying the molecular triggers of early lineage commitment in embryonic stem cells. It was during this time that I formulated the ideas for my long term research plans for studying the molecular structure and function of the synaptonemal complex in meiosis. Over the last three years, I have initiated this research at the Department of Biochemistry, University of Cambridge, working with Dr. Luca Pellegrini.
Owen has already relocated to Newcastle and has started work in ICaMB
Dr Josana Rodriguez
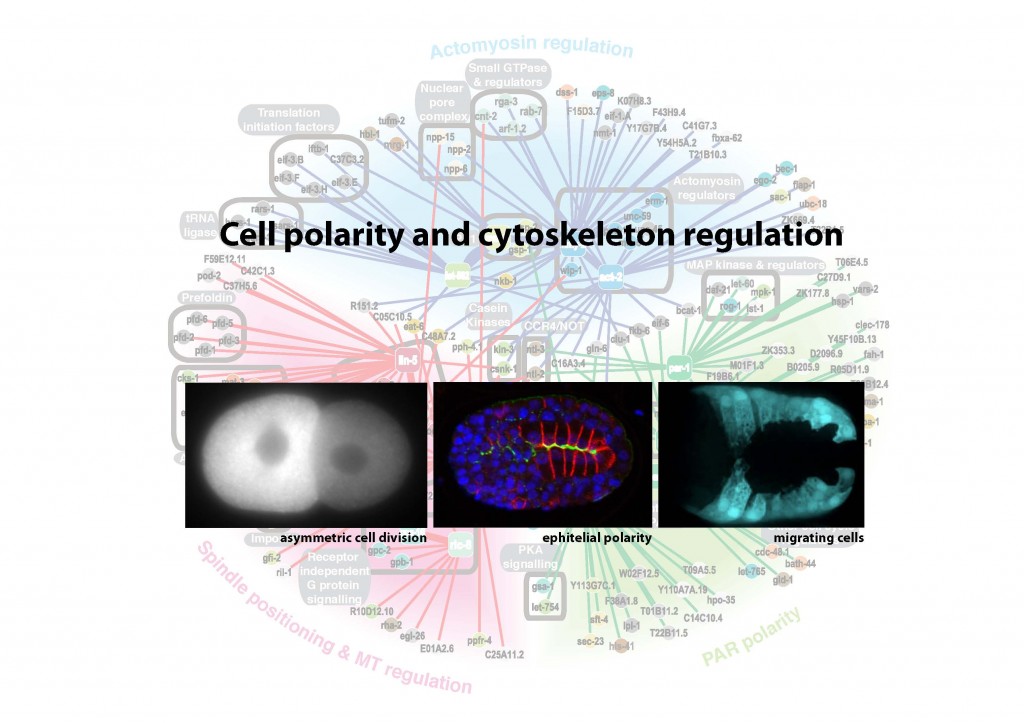
 Research interest: By breaking symmetry, cells are able to generate diversity, migrate, and organise themselves into more complex structures such as tissues and organs. Misregulation of such cell polarity is implicated in a number of human diseases, most notably cancer. Tumour progression is correlated with disruption of epithelial polarity and randomized orientation of the cell division plane caused by misplacement of the mitotic spindle. These observations show the importance of cell polarity for the correct development of an organism and the tight regulation required between cell polarity mechanisms and the cytoskeleton.
Research interest: By breaking symmetry, cells are able to generate diversity, migrate, and organise themselves into more complex structures such as tissues and organs. Misregulation of such cell polarity is implicated in a number of human diseases, most notably cancer. Tumour progression is correlated with disruption of epithelial polarity and randomized orientation of the cell division plane caused by misplacement of the mitotic spindle. These observations show the importance of cell polarity for the correct development of an organism and the tight regulation required between cell polarity mechanisms and the cytoskeleton.
My aim is to identify new interactions between cell polarity and the cytoskeleton, and to understand them in a whole organism context during morphogenetic movements and tissue organisation. I would like to extend these studies to analyse the possible implication of these interactions in diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Background: I am currently a postdoctoral research fellow at The Gurdon Institute (Wellcome Trust/Cancer Research, UK) working in the laboratory of Dr. Julie Ahringer (2006 to date). My postdoctoral research identified genes involved in the polarisation of cells through high-throughput genetic screens in C. elegans. I have been a Wolfson College Fellow since 2009 (University of Cambridge).
Josana plans to relocate to Newcastle in July 2014 after completing some ongoing studies in Cambridge
Dr Niall Kenneth
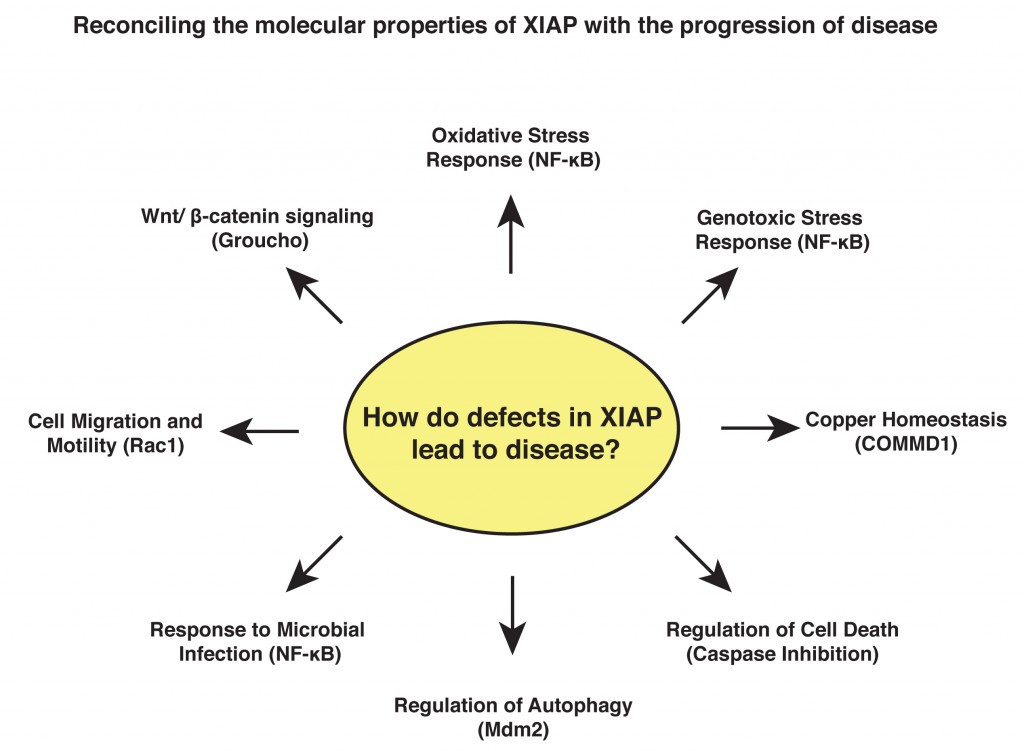
 Research Interests: My work focuses on the signalling properties of a family of intracellular proteins called the IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis). These proteins were originally characterised as modulators of cell death but have since emerged as key signalling intermediates that regulate a variety of cellular functions. X-linked IAP (XIAP) has been the subject of much recent interest as a possible therapeutic target in cancer due to its greatly elevated expression in tumour cells and its well-documented ability to inhibit cell death. Additional work has identified germline mutations in the XIAP gene that cause a severe primary immunodeficiency known as X-linked lymphoproliferative disorder (XLPD). My work aims to understand the role played by XIAP in essential cellular processes and to reconcile this with its role in pathogenesis.
Research Interests: My work focuses on the signalling properties of a family of intracellular proteins called the IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis). These proteins were originally characterised as modulators of cell death but have since emerged as key signalling intermediates that regulate a variety of cellular functions. X-linked IAP (XIAP) has been the subject of much recent interest as a possible therapeutic target in cancer due to its greatly elevated expression in tumour cells and its well-documented ability to inhibit cell death. Additional work has identified germline mutations in the XIAP gene that cause a severe primary immunodeficiency known as X-linked lymphoproliferative disorder (XLPD). My work aims to understand the role played by XIAP in essential cellular processes and to reconcile this with its role in pathogenesis.
Background: After my PhD, I joined the group of Dr Sonia Rocha at the Centre of Gene Regulation and Expression at the University of Dundee, where I focused on the control of gene transcription following DNA damage and hypoxic stress, regulated by the NF-kB and HIF transcription factors. In 2010, I relocated to the USA to join the laboratory of Professor Colin Duckett, at the University of Michigan, where I have continued to work on transcriptional regulation and developed my interests in the IAP proteins and how they are altered in disease.
Niall will relocate to Newcastle in April 2014
Royal Society University Research Fellowship
The Royal Society URF is one of the most prestigious fellowships awarded to young scientists seeking an independent research career. We are therefore extremely happy that based on her outstanding postdoctoral work in ICaMB, Yulia Yuzenkova has recently received this award.
Dr Yulia Yuzenkova
 Research Interests: My research is focussed on mechanisms of gene expression in cyanobacteria, one of the most ancient and ecologically important, but under-studied group of organisms on Earth. Approximately 2.3 billion years ago cyanobacteria invented photosynthesis, which transformed all subsequent biological history of Earth. Nowadays they live everywhere where sunlight is available and produce 30% of atmospheric oxygen; furthermore, they can convert inert atmospheric nitrogen to the forms digestible by other organisms. I will be working on transcription in cyanobacteria and its coordination with other major processes in the cell, such as DNA replication and translation.
Research Interests: My research is focussed on mechanisms of gene expression in cyanobacteria, one of the most ancient and ecologically important, but under-studied group of organisms on Earth. Approximately 2.3 billion years ago cyanobacteria invented photosynthesis, which transformed all subsequent biological history of Earth. Nowadays they live everywhere where sunlight is available and produce 30% of atmospheric oxygen; furthermore, they can convert inert atmospheric nitrogen to the forms digestible by other organisms. I will be working on transcription in cyanobacteria and its coordination with other major processes in the cell, such as DNA replication and translation.
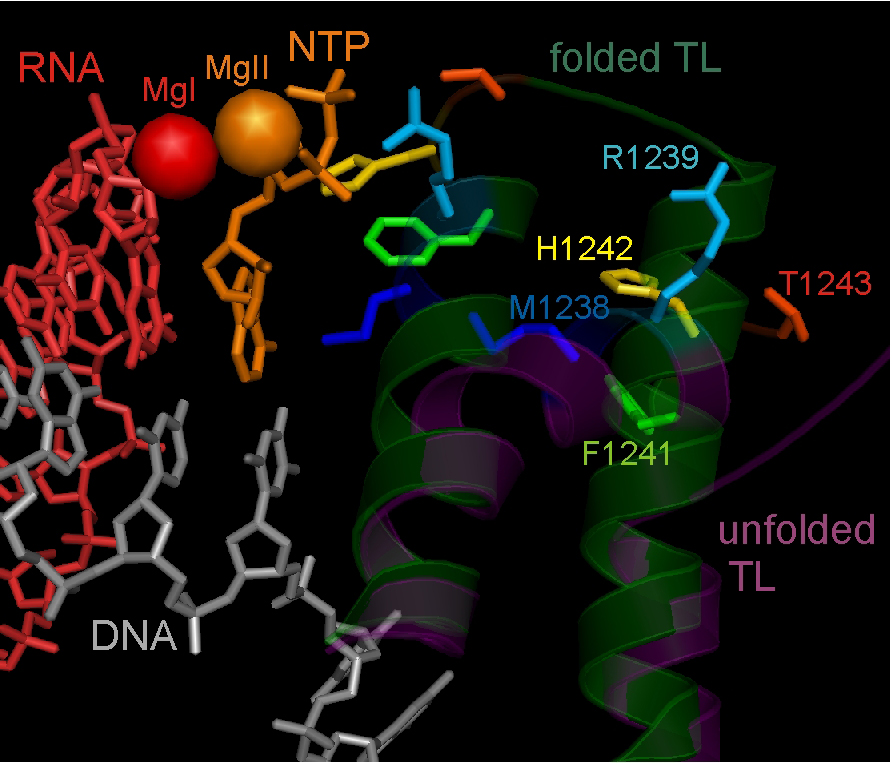
Active centre of the T. thermophilus RNAP elongation complex with unfolded (inactive) and folded (active) Trigger Loop domain conformation.
Background: I did my PhD in the Institute of Molecular Genetics in Moscow and then my first PostDoc in the Waksman Institute in Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey, USA where I performed structure-functional studies of bacterial RNA polymerase. After moving to Newcastle University, I have been working on a variety of projects investigating the mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by bacterial RNA Polymerase.
New ICaMB Professor
In addition to our new young PIs, we have also recruited a new young(ish) Professor, Jonathan Higgins from the Brigham and Women’s Hospital at Harvard Medical School
Prof Jonathan Higgins
 Research Interests: Cell division is a short but dramatic part of the cell cycle. To ensure precise inheritance of the genetic material, chromosomes must be disentangled, condensed, and then “bi-oriented” on microtubules so that they can be sorted properly into the daughter cells. My lab aims to understand fundamental processes that control these events: specifically, the post-translational modifications of histone proteins that dictate recruitment and displacement of regulatory proteins to and from chromatin during cell division. In particular, my lab has revealed the role of histone kinases such as Haspin in localizing key “error-correcting” proteins to centromeres in mitosis.
Research Interests: Cell division is a short but dramatic part of the cell cycle. To ensure precise inheritance of the genetic material, chromosomes must be disentangled, condensed, and then “bi-oriented” on microtubules so that they can be sorted properly into the daughter cells. My lab aims to understand fundamental processes that control these events: specifically, the post-translational modifications of histone proteins that dictate recruitment and displacement of regulatory proteins to and from chromatin during cell division. In particular, my lab has revealed the role of histone kinases such as Haspin in localizing key “error-correcting” proteins to centromeres in mitosis.
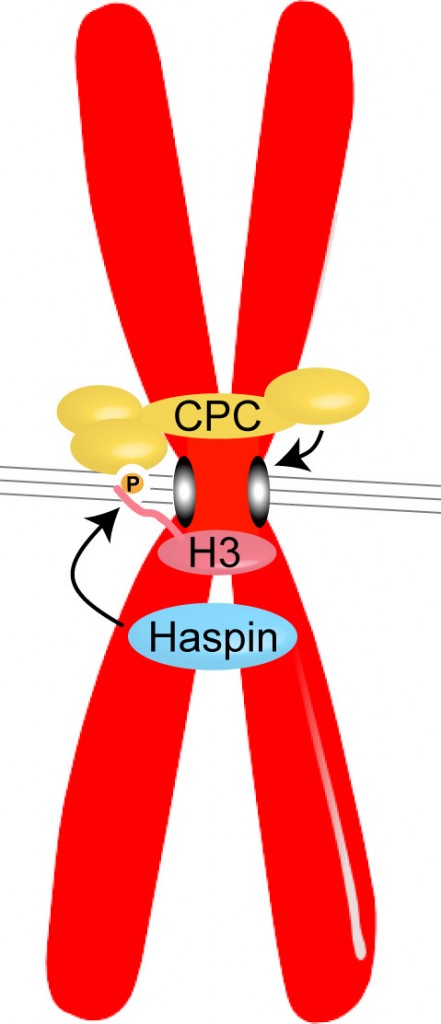 Haspin phosphorylates Histone H3 to create a binding site for the Chromosomal Passenger Complex (CPC) at the centromeres of chromosomes in mitosis. The CPC, which contains the kinase Aurora B, acts to prevent incorrect attachments of microtubules (grey lines) to kinetochores (grey ovals), to ensure the appropriate segregation of chromosomes during cell division.
Haspin phosphorylates Histone H3 to create a binding site for the Chromosomal Passenger Complex (CPC) at the centromeres of chromosomes in mitosis. The CPC, which contains the kinase Aurora B, acts to prevent incorrect attachments of microtubules (grey lines) to kinetochores (grey ovals), to ensure the appropriate segregation of chromosomes during cell division.
Background: I was born in Stockton-on-Tees and grew up in North Yorkshire. During my postdoc with Michael Brenner at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), Harvard Medical School (HMS), I discovered a novel gene, which turned out to be Haspin, within an intron of the integrin gene I was studying. I started working on Haspin as a side project, and then more seriously when I joined the faculty at BWH/HMS to set up my own research group.
Jonathan will relocate permanently to Newcastle in July 2014
The next generation of ICaMB PIs and Research Fellows
Owen, Josana, Niall, Yulia and Jonathan join a growing group of new PIs in ICaMB, which include 2 further Royal Society URF award winners together with recipients of Wellcome Trust/Royal Society Henry Dale and Career Re-entry Fellowships. We are confident that their talent drive, and enthusiasm will ensure a bright future for research in Cell and Molecular Biosciences in Newcastle.
Dr Suzanne Madgwick: Suzanne is a Wellcome Trust Career Re-entry Fellow researching mechanisms of meiosis
Dr Heath Murray: Heath is a Royal Society University Research Fellow researching the Regulation of Bacterial DNA Replication Initiation
Dr Paula Salgado: Paula is a Lecturer in Macromolecular Crystallography studying the mechanisms of host-pathogen interactions
Dr Claudia Schneider: is a Royal Society University Research Fellow investigating nonsense mediated mRNA decay pathways
Dr Kevin Waldron: is a Wellcome Trust/Royal Society Henry Dale Fellow investigating the role of essential metal ions in pathogenic bacteria