As we develop our understanding of AI and its capabilities, we are looking at how advancing technologies such as ChatGPT might assist colleagues and students with day to day tasks. FMS TEL team members Simon Cotterill, Gemma Mitchelson and Michael Hughes succeeded in securing ERDP funding to explore such possibilities.
Project aims:
- To enable staff and students to access contextualised and personal data via AI machine learning software
- To investigate a process for generating AI responses in a more ethical way
- To improve the University’s understanding of AI machine learning in an HE context.
We are investigating use of contextualised data, formatted with natural language, optimized for A.I. For example, using a student’s programme and module information, their timetable data, and MOF information to assist the student in accessing key information more easily. Later this could be enhanced with richer information, such as programme/module study guides, VLE course information and other sources. via APIs. Likewise, a chatbot for staff could draw together University, Faculty and School-specific information.
An exciting new feature to be explored is that of agents (aka ‘Assistants’) and their ability to take on different functions and different personas; effectively acting as a small workforce to support, user needs. Up to now, most of us are familiar with having a conversation with a single agent, yet there is growing scope for multi-agent use. In the visual below you can see an Ai Agents overview from Chat Dev. By setting instructions and ’embedding’ information into the system users can encourage each agent to behave differently. For example, “You are a member of the Design team who will come up with simple ways to achieve a set goal”, “You are a CEO who will talk to the CTO on what steps should be taken to achieve X,Y and Z.”…
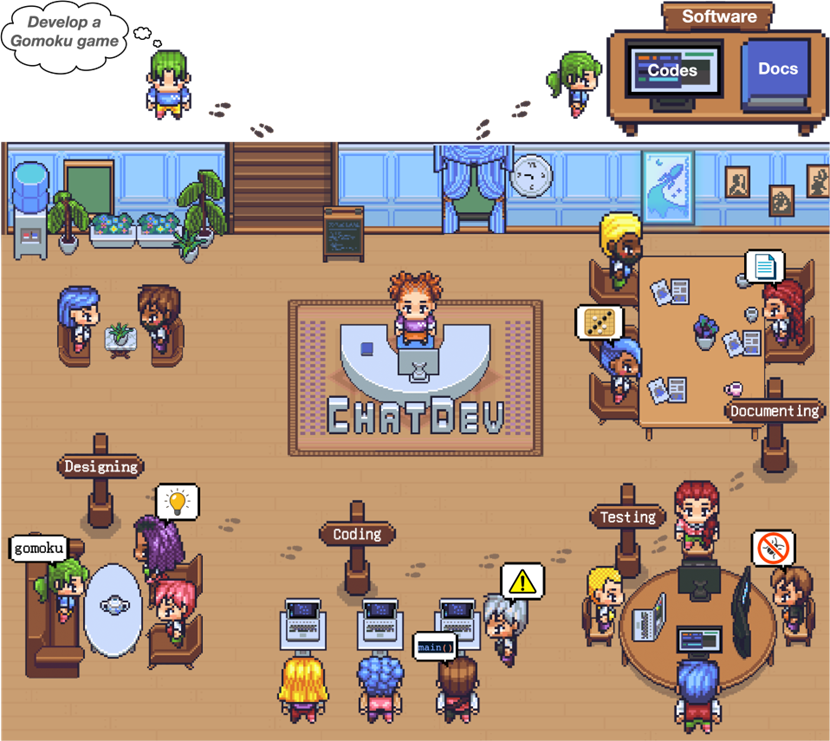

image source: https://github.com/OpenBMB/ChatDev
The technologies are evolving very rapidly. At an “AI Sprint” in late November, the FMS TEL team were able to work with newly released features from OpenAI; these make the embedding of customised information and personalising Assistants (agents) much more accessible. These and other new features support the integration of AI features within other systems. As such, there is likely to be a proliferation of new AI products and plugins based on these features – and hopefully eventually within the systems supported by FMS TEL. All work in our project will be cross-referenced to our university principles on AI which can be accessed here: Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Learning and Teaching @ Newcastle | Newcastle University (ncl.ac.uk)
There are challenges to consider; in particular those related to Data Protection, which we continue to review. There are also financial considerations when using external AI services like OpenAI or via Azure API, which are metered (pay according to use), rather than fixed price plans, which need investigating as part of our intended trial/pilot.
We are in the early stages of fact-finding but will be reaching out to FMS schools in the new year with an invite to workshops to share our proof of concept.