Ann Johnson has been a Patient and Public Involvement (PPI) Advocate, Lay tutor, and facilitator for twenty-five years, researching and creating a Patient Involvement Framework for Leicester University Medical School. She has conducted extensive community outreach in London, Leicester, and Florida USA with the goal of bridging communications between patients and practitioners. She is continuing her work as an Associate Lecturer and PPI Advocate at the School of Medicine.
As part of this module, it was important to ensure that a patient-centred approach to healthcare was highlighted. As such, Ann’s experience in the field allowed her to challenge students to look at healthcare – and clinical trials in particular – from the patients’ points of view.
One particular topic inspired Ann to focus on the topic of unconscious bias in more detail. In cases of hypertension, GPs had been trained to prescribe different drugs and treatment plans to people based on ethnicity, even though there is no evidence to support this course of action (Gopal, D.P. et al., 2022). This is an example of taught bias – but at the same time, GPs were making assumptions about patients’ ethnicities which could also be erroneous. Naturally, this is an area of concern for patients.
Equality, Diversity and Inclusion and Bias
The difference between EDI concerns and bias is important to clarify at this stage. While EDI principles are focused on actively working to improve outcomes, unconscious bias is present in all of us as a survival instinct and extends beyond those ‘protected characteristics’ formalised in EDI policies. Unconscious bias allows us to make quick decisions based on assumptions – for example choosing to cross the road to avoid encountering someone walking along with an unleashed Pitbull Terrier.
As a clinician, it is especially important to recognise one’s own potential for unconscious bias as it can affect decision-making, resulting in poorer outcomes for some patients. When this bias extends to choosing who to include in clinical trials, it is easy to see how misconceptions or omissions could be compounded.
Discussion
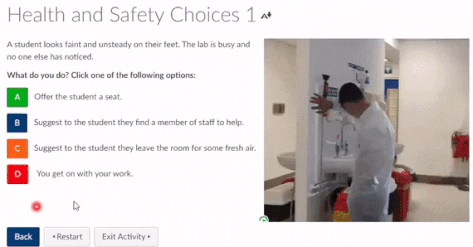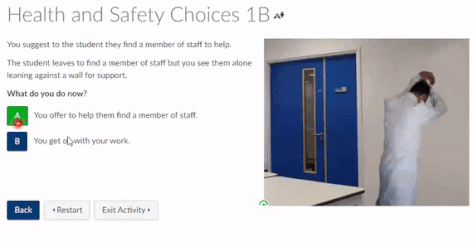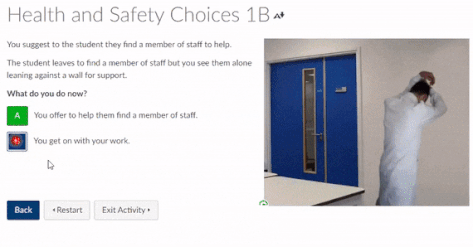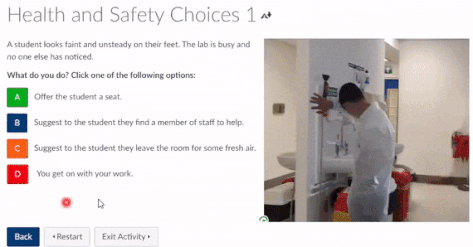
You have been asked to become involved with the recruitment for the trial of Nosuchximab, a targeted therapy for Paediatric Lymphoma. The research target group is children aged between 02 and 14. There is a significant disparity in survival rates of the South Asian population and white European population. You have been asked to recruit children from the target age range. However, the NHS Foundation Trust site for the Nosuchximab trial is located within in a region where this population is under-represented – however, it is present (although in minimal number).
- How might Unconscious Bias impact the outcomes of this trial?
- Is it important to strategically recruit this cohort?
- How might you put in place a strategy for recruiting those particular subjects?
- What attempts should be made to minimalize barriers to their inclusion?
The above activity challenges students to consider a range of complex factors and is designed to explore the recruitment process for clinical trials, which can be affected by unconscious bias. As such, we designed a range of scaffolding activities to lead up to students exploring this topic in a more confident and informed manner.
The learning was divided into three stages, supported by Canvas’ tools.
- An introduction to unconscious bias with a test-your-knowledge quiz. This built understanding of the basics, and used the quiz to instil confidence into the students that they had understood the basics. The introduction was also written in such a way to highlight that this was a supportive environment.
- An opportunity to explore the effect of unconscious bias through a key reading, and a test that students could try to identify their own potential biases, followed by reflection in one of a few ways.
- Attempt the activity in discussion with others. A webinar is also available for students to join and discuss the activity with Ann and the other students, as well as to explore the topic further if needed.
We understood that the topic of unconscious bias could be challenging for students to confront, as it is intensely personal and potentially triggering. To allow students to explore this area in a supportive way, we suggested a range of activities, from private reflection to group discussion, about the topic in general, to allow students to examine this in an environment where they felt comfortable. We felt that this was especially important as this meant students would not feel they may be judged or blamed for sharing their experiences and feelings about bias, and this would make the entire topic much more approachable, and the learning more effective.
Next Steps
The activities will soon be live for students to try out the materials and share feedback. Anything highlighted by the student feedback will be discussed, and appropriate changes made to the activities if necessary. These materials will then run as part of the module next year. Further distribution of this content can also be done via Canvas Commons, should other module leaders wish to incorporate them into their teaching.
References
Gopal, D.P., Okoli, G.N. & Rao, M. Re-thinking the inclusion of race in British hypertension guidance. J Hum Hypertens 36, 333–335 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-021-00601-9